 |
MPTRAC
|
 |
MPTRAC
|
MPTRAC library declarations. More...
#include <ctype.h>#include <gsl/gsl_fft_complex.h>#include <gsl/gsl_math.h>#include <gsl/gsl_randist.h>#include <gsl/gsl_rng.h>#include <gsl/gsl_sort.h>#include <gsl/gsl_spline.h>#include <gsl/gsl_statistics.h>#include <math.h>#include <netcdf.h>#include <omp.h>#include <stdint.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <string.h>#include <time.h>#include <sys/time.h>Go to the source code of this file.
Data Structures | |
| struct | ctl_t |
| Control parameters. More... | |
| struct | atm_t |
| Air parcel data. More... | |
| struct | particle_t |
| Particle data. More... | |
| struct | cache_t |
| Cache data structure. More... | |
| struct | clim_photo_t |
| Climatological data in the form of photolysis rates. More... | |
| struct | clim_ts_t |
| Climatological data in the form of time series. More... | |
| struct | clim_zm_t |
| Climatological data in the form of zonal means. More... | |
| struct | clim_t |
| Climatological data. More... | |
| struct | met_t |
| Meteo data structure. More... | |
| struct | dd_t |
| Domain decomposition data structure. More... | |
Macros | |
| #define | MPI_Datatype void* |
| Placeholder when MPI is not available. More... | |
| #define | codes_handle void* |
| Placeholder when ECCODES is not available. More... | |
| #define | AVO 6.02214076e23 |
| Avogadro constant [1/mol]. More... | |
| #define | CPD 1003.5 |
| Specific heat of dry air at constant pressure [J/(kg K)]. More... | |
| #define | EPS (MH2O / MA) |
| Ratio of the specific gas constant of dry air and water vapor [1]. More... | |
| #define | G0 9.80665 |
| Standard gravity [m/s^2]. More... | |
| #define | H0 7.0 |
| Scale height [km]. More... | |
| #define | LV 2501000. |
| Latent heat of vaporization of water [J/kg]. More... | |
| #define | KARMAN 0.40 |
| Karman's constant. More... | |
| #define | KB 1.3806504e-23 |
| Boltzmann constant [kg m^2/(K s^2)]. More... | |
| #define | MA 28.9644 |
| Molar mass of dry air [g/mol]. More... | |
| #define | MH2O 18.01528 |
| Molar mass of water vapor [g/mol]. More... | |
| #define | MO3 48.00 |
| Molar mass of ozone [g/mol]. More... | |
| #define | P0 1013.25 |
| Standard pressure [hPa]. More... | |
| #define | RA (1e3 * RI / MA) |
| Specific gas constant of dry air [J/(kg K)]. More... | |
| #define | RE 6367.421 |
| Mean radius of Earth [km]. More... | |
| #define | RI 8.3144598 |
| Ideal gas constant [J/(mol K)]. More... | |
| #define | T0 273.15 |
| Standard temperature [K]. More... | |
| #define | EP 140 |
| Maximum number of pressure levels for meteo data. More... | |
| #define | EX 1444 |
| Maximum number of longitudes for meteo data. More... | |
| #define | EY 724 |
| Maximum number of latitudes for meteo data. More... | |
| #define | LEN 5000 |
| Maximum length of ASCII data lines. More... | |
| #define | METVAR 13 |
| Number of 3-D meteorological variables. More... | |
| #define | NP 10000000 |
| Maximum number of atmospheric data points. More... | |
| #define | NQ 15 |
| Maximum number of quantities per data point. More... | |
| #define | NCSI 1000000 |
| Maximum number of data points for CSI calculation. More... | |
| #define | NENS 2000 |
| Maximum number of data points for ensemble analysis. More... | |
| #define | NOBS 10000000 |
| Maximum number of observation data points. More... | |
| #define | NTHREADS 512 |
| Maximum number of OpenMP threads. More... | |
| #define | CY 250 |
| Maximum number of latitudes for climatological data. More... | |
| #define | CO3 30 |
| Maximum number of total column ozone data for climatological data. More... | |
| #define | CP 70 |
| Maximum number of pressure levels for climatological data. More... | |
| #define | CSZA 50 |
| Maximum number of solar zenith angles for climatological data. More... | |
| #define | CT 12 |
| Maximum number of time steps for climatological data. More... | |
| #define | CTS 1000 |
| Maximum number of data points of climatological time series. More... | |
| #define | DD_NPART 100000 |
| Maximum number of particles to send and recieve in domain decomposition. More... | |
| #define | DD_NNMAX 26 |
| Maximum number of neighbours to communicate with in domain decomposition. More... | |
| #define | DD_NPOLE -2 |
| Constant indicating the North pole [-]. More... | |
| #define | DD_SPOLE -3 |
| Constant indicating the South pole [-]. More... | |
| #define | ALLOC(ptr, type, n) |
| Allocate memory for a pointer with error handling. More... | |
| #define | ARRAY_2D(ix, iy, ny) ((ix) * (ny) + (iy)) |
| Macro for computing the linear index of a 2D array element. More... | |
| #define | ARRAY_3D(ix, iy, ny, iz, nz) (((ix)*(ny) + (iy)) * (nz) + (iz)) |
| Compute the linear index of a 3D array element. More... | |
| #define | ARRHENIUS(a, b, t) ((a) * exp( -(b) / (t))) |
| Calculate the Arrhenius rate constant. More... | |
| #define | CLAMP(v, lo, hi) (((v) < (lo)) ? (lo) : (((v) > (hi)) ? (hi) : (v))) |
| Clamp a value to a specified range. More... | |
| #define | DEG2DX(dlon, lat) (RE * DEG2RAD(dlon) * cos(DEG2RAD(lat))) |
| Convert a longitude difference to a distance in the x-direction (east-west) at a specific latitude. More... | |
| #define | DEG2DY(dlat) (RE * DEG2RAD(dlat)) |
| Convert a latitude difference to a distance in the y-direction (north-south). More... | |
| #define | DEG2RAD(deg) ((deg) * (M_PI / 180.0)) |
| Converts degrees to radians. More... | |
| #define | DP2DZ(dp, p) (- (dp) * H0 / (p)) |
| Convert a pressure difference to a height difference in the vertical direction. More... | |
| #define | DX2DEG(dx, lat) |
| Convert a distance in kilometers to degrees longitude at a given latitude. More... | |
| #define | DY2DEG(dy) ((dy) * 180. / (M_PI * RE)) |
| Convert a distance in kilometers to degrees latitude. More... | |
| #define | DZ2DP(dz, p) (-(dz) * (p) / H0) |
| Convert a change in altitude to a change in pressure. More... | |
| #define | DIST(a, b) sqrt(DIST2(a, b)) |
| Calculate the distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates. More... | |
| #define | DIST2(a, b) ((a[0]-b[0])*(a[0]-b[0])+(a[1]-b[1])*(a[1]-b[1])+(a[2]-b[2])*(a[2]-b[2])) |
| Calculate the squared Euclidean distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates. More... | |
| #define | DOTP(a, b) (a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1]+a[2]*b[2]) |
| Calculate the dot product of two vectors. More... | |
| #define | ECC(cmd) |
| Execute an ECCODES command and check for errors. More... | |
| #define | ECC_READ_2D(variable, target, scaling_factor, found_flag) |
| Writes 2-D data from a grib message into the meteo struct. More... | |
| #define | ECC_READ_3D(variable, level, target, scaling_factor, found_flag) |
| Writes 3D data from a grib message into the meteo struct. More... | |
| #define | FMOD(x, y) ((x) - (int) ((x) / (y)) * (y)) |
| Calculate the floating-point remainder of dividing x by y. More... | |
| #define | FREAD(ptr, type, size, in) |
| Read data from a file stream and store it in memory. More... | |
| #define | FWRITE(ptr, type, size, out) |
| Write data from memory to a file stream. More... | |
| #define | INTPOL_INIT double cw[4] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0}; int ci[3] = {0, 0, 0}; |
| Initialize arrays for interpolation. More... | |
| #define | INTPOL_2D(var, init) |
| Perform 2D interpolation for a meteorological variable. More... | |
| #define | INTPOL_3D(var, init) |
| Perform 3D interpolation for a meteorological variable. More... | |
| #define | INTPOL_SPACE_ALL(p, lon, lat) |
| Interpolate multiple meteorological variables in space. More... | |
| #define | INTPOL_TIME_ALL(time, p, lon, lat) |
| Interpolate multiple meteorological variables in time. More... | |
| #define | LAPSE(p1, t1, p2, t2) |
| Calculate lapse rate. More... | |
| #define | LIN(x0, y0, x1, y1, x) ((y0)+((y1)-(y0))/((x1)-(x0))*((x)-(x0))) |
| Linear interpolation. More... | |
| #define | MAX(a, b) (((a)>(b))?(a):(b)) |
| Macro to determine the maximum of two values. More... | |
| #define | MET_HEADER |
| Write header for meteorological data file. More... | |
| #define | MIN(a, b) (((a)<(b))?(a):(b)) |
| Macro to determine the minimum of two values. More... | |
| #define | MOLEC_DENS(p, t) (AVO * 1e-6 * ((p) * 100) / (RI * (t))) |
| Calculate the density of a gas molecule. More... | |
| #define | NC(cmd) |
| Execute a NetCDF command and check for errors. More... | |
| #define | NC_DEF_VAR(varname, type, ndims, dims, long_name, units, level, quant) |
| Define a NetCDF variable with attributes. More... | |
| #define | NC_GET_DOUBLE(varname, ptr, force) |
| Retrieve a double-precision variable from a NetCDF file. More... | |
| #define | NC_INQ_DIM(dimname, ptr, min, max, check) |
| Inquire the length of a dimension in a NetCDF file. More... | |
| #define | NC_PUT_DOUBLE(varname, ptr, hyperslab) |
| Write double precision data to a NetCDF variable. More... | |
| #define | NC_PUT_FLOAT(varname, ptr, hyperslab) |
| Write a float array to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| #define | NC_PUT_INT(varname, ptr, hyperslab) |
| Write integer data to a NetCDF variable. More... | |
| #define | NC_PUT_ATT(varname, attname, text) |
| Add a text attribute to a NetCDF variable. More... | |
| #define | NC_PUT_ATT_GLOBAL(attname, text) NC(nc_put_att_text(ncid, NC_GLOBAL, attname, strnlen(text, LEN), text)); |
| Add a global text attribute to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| #define | NN(x0, y0, x1, y1, x) (fabs((x) - (x0)) <= fabs((x) - (x1)) ? (y0) : (y1)) |
| Perform nearest-neighbor interpolation. More... | |
| #define | PARTICLE_LOOP(ip0, ip1, check_dt, ...) |
| Loop over particle indices with OpenACC acceleration. More... | |
| #define | P(z) (P0 * exp(-(z) / H0)) |
| Compute pressure at given altitude. More... | |
| #define | PSAT(t) (6.112 * exp(17.62 * ((t) - T0) / (243.12 + (t) - T0))) |
| Compute saturation pressure over water. More... | |
| #define | PSICE(t) (6.112 * exp(22.46 * ((t) - T0) / (272.62 + (t) - T0))) |
| Compute saturation pressure over ice (WMO, 2018). More... | |
| #define | PW(p, h2o) ((p) * MAX((h2o), 0.1e-6) / (1. + (1. - EPS) * MAX((h2o), 0.1e-6))) |
| Calculate partial water vapor pressure. More... | |
| #define | RAD2DEG(rad) ((rad) * (180.0 / M_PI)) |
| Converts radians to degrees. More... | |
| #define | RH(p, t, h2o) (PW(p, h2o) / PSAT(t) * 100.) |
| Compute relative humidity over water. More... | |
| #define | RHICE(p, t, h2o) (PW(p, h2o) / PSICE(t) * 100.) |
| Compute relative humidity over ice. More... | |
| #define | RHO(p, t) (100. * (p) / (RA * (t))) |
| Compute density of air. More... | |
| #define | SET_ATM(qnt, val) |
| Set atmospheric quantity value. More... | |
| #define | SET_QNT(qnt, name, longname, unit) |
| Set atmospheric quantity index. More... | |
| #define | SH(h2o) (EPS * MAX((h2o), 0.1e-6)) |
| Compute specific humidity from water vapor volume mixing ratio. More... | |
| #define | SQR(x) ((x)*(x)) |
| Compute the square of a value. More... | |
| #define | SWAP(x, y, type) do {type tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp;} while(0); |
| Swap two values. More... | |
| #define | TDEW(p, h2o) |
| Calculate dew point temperature. More... | |
| #define | TICE(p, h2o) |
| Calculate frost point temperature (WMO, 2018). More... | |
| #define | THETA(p, t) ((t) * pow(1000. / (p), 0.286)) |
| Compute potential temperature. More... | |
| #define | THETAVIRT(p, t, h2o) (TVIRT(THETA((p), (t)), MAX((h2o), 0.1e-6))) |
| Compute virtual potential temperature. More... | |
| #define | TOK(line, tok, format, var) |
| Get string tokens. More... | |
| #define | TVIRT(t, h2o) ((t) * (1. + (1. - EPS) * MAX((h2o), 0.1e-6))) |
| Compute virtual temperature. More... | |
| #define | Z(p) (H0 * log(P0 / (p))) |
| Convert pressure to altitude. More... | |
| #define | ZDIFF(lnp0, t0, h2o0, lnp1, t1, h2o1) |
| Calculate geopotential height difference. More... | |
| #define | ZETA(ps, p, t) |
| Computes the value of the zeta vertical coordinate. More... | |
| #define | LOGLEV 2 |
| Level of log messages (0=none, 1=basic, 2=detailed, 3=debug). More... | |
| #define | LOG(level, ...) |
| Print a log message with a specified logging level. More... | |
| #define | WARN(...) |
| Print a warning message with contextual information. More... | |
| #define | ERRMSG(...) |
| Print an error message with contextual information and terminate the program. More... | |
| #define | PRINT(format, var) |
| Print the value of a variable with contextual information. More... | |
| #define | NTIMER 100 |
| Maximum number of timers. More... | |
| #define | PRINT_TIMERS timer("END", "END", 1); |
| Print the current state of all timers. More... | |
| #define | SELECT_TIMER(id, group) timer(id, group, 0); |
| Select and start a timer with specific attributes. More... | |
Functions | |
| void | broadcast_large_data (void *data, size_t N) |
| Broadcasts large data across all processes in an MPI communicator. More... | |
| void | cart2geo (const double *x, double *z, double *lon, double *lat) |
| Converts Cartesian coordinates to geographic coordinates. More... | |
| double | clim_oh (const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, const double t, const double lon, const double lat, const double p) |
| Calculates the hydroxyl radical (OH) concentration from climatology data, with an optional diurnal correction based on solar zenith angle. More... | |
| void | clim_oh_diurnal_correction (const ctl_t *ctl, clim_t *clim) |
| Applies a diurnal correction to the hydroxyl radical (OH) concentration in climatology data. More... | |
| double | clim_photo (const double rate[CP][CSZA][CO3], const clim_photo_t *photo, const double p, const double sza, const double o3c) |
| Calculates the photolysis rate for a given set of atmospheric conditions. More... | |
| double | clim_tropo (const clim_t *clim, const double t, const double lat) |
| Calculates the tropopause pressure based on climatological data. More... | |
| void | clim_tropo_init (clim_t *clim) |
| Initializes the tropopause data in the climatology structure. More... | |
| double | clim_ts (const clim_ts_t *ts, const double t) |
| Interpolates a time series of climatological variables. More... | |
| double | clim_zm (const clim_zm_t *zm, const double t, const double lat, const double p) |
| Interpolates monthly mean zonal mean climatological variables. More... | |
| void | compress_cms (const ctl_t *ctl, const char *varname, float *array, const size_t nx, const size_t ny, const size_t np, const double *plev, const int decompress, FILE *inout) |
| Compresses or decompresses a 3-D meteorological field using cmultiscale. More... | |
| void | compress_pck (const char *varname, float *array, const size_t nxy, const size_t nz, const int decompress, FILE *inout) |
| Compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats. More... | |
| void | compress_sz3 (const char *varname, float *array, const int nx, const int ny, const int nz, const int precision, const double tolerance, const int decompress, FILE *inout) |
| Compresses or decompresses a 3-D float array using the SZ3 library. More... | |
| void | compress_zfp (const char *varname, float *array, const int nx, const int ny, const int nz, const int precision, const double tolerance, const int decompress, FILE *inout) |
| Compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats using the ZFP library. More... | |
| void | compress_zstd (const char *varname, float *array, const size_t n, const int decompress, const int level, FILE *inout) |
| Compresses or decompresses a float array using Zstandard (ZSTD). More... | |
| double | cos_sza (const double sec, const double lon, const double lat) |
| Calculates the cosine of the solar zenith angle. More... | |
| void | day2doy (const int year, const int mon, const int day, int *doy) |
| Get day of year from date. More... | |
| void | dd_assign_rect_subdomains_atm (atm_t *atm, ctl_t *ctl, dd_t *dd, int init) |
| Assign atmospheric particles to rectangular subdomains. More... | |
| void | dd_atm2particles (atm_t *atm, particle_t *particles, ctl_t *ctl, int *nparticles, cache_t *cache, int rank) |
| Extracts particles from an atmospheric state and prepares them for inter-domain transfer. More... | |
| int | dd_calc_subdomain_from_coords (double lon, double lat, met_t *met, ctl_t *ctl, int mpi_size, int nx_glob, int ny_glob) |
| Computes the destination subdomain (MPI rank) for a particle based on its geographic coordinates. More... | |
| void | dd_communicate_particles (particle_t *particles, int *nparticles, MPI_Datatype MPI_Particle, int *neighbours, int nneighbours, ctl_t ctl) |
| Communicates particles between MPI processes. More... | |
| void | dd_get_rect_neighbour (const ctl_t ctl, dd_t *dd) |
| Determines rectangular neighbouring ranks for MPI processes. More... | |
| int | dd_init (ctl_t *ctl, dd_t *dd, atm_t *atm) |
| Initializes domain decomposition for parallel processing. More... | |
| int | dd_is_periodic_longitude (met_t *met, int nx_glob) |
| Check whether the longitude grid is periodic (global coverage). More... | |
| void | dd_particles2atm (atm_t *atm, particle_t *particles, ctl_t *ctl, int *nparticles, cache_t *cache) |
| Converts particle data to atmospheric data. More... | |
| void | dd_register_MPI_type_particle (MPI_Datatype *MPI_Particle) |
| Registers a custom MPI datatype for particle structures. More... | |
| void | dd_sort (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, atm_t *atm, dd_t *dd, int *nparticles, int *rank) |
| Sort particles according to box index and target rank for neighbours. More... | |
| void | dd_sort_help (double *a, dd_t *dd, const int np) |
| Reorder an array according to a permutation vector. More... | |
| void | doy2day (const int year, const int doy, int *mon, int *day) |
| Converts a given day of the year (DOY) to a date (month and day). More... | |
| void | fft_help (double *fcReal, double *fcImag, const int n) |
| Computes the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of a complex sequence. More... | |
| void | geo2cart (const double z, const double lon, const double lat, double *x) |
| Converts geographic coordinates (longitude, latitude, altitude) to Cartesian coordinates. More... | |
| void | get_met_help (const ctl_t *ctl, const double t, const int direct, const char *metbase, const double dt_met, char *filename) |
| Generates a formatted filename for meteorological data files based on the input parameters. More... | |
| void | get_met_replace (char *orig, char *search, char *repl) |
| Replaces occurrences of a substring in a string with another substring. More... | |
| void | get_tropo (const int met_tropo, ctl_t *ctl, clim_t *clim, met_t *met, const double *lons, const int nx, const double *lats, const int ny, double *pt, double *zt, double *tt, double *qt, double *o3t, double *ps, double *zs) |
| Calculate tropopause data. More... | |
| void | intpol_check_lon_lat (const double *lons, const int nlon, const double *lats, const int nlat, const double lon, const double lat, double *lon2, double *lat2) |
| Adjusts longitude and latitude to ensure they fall within valid bounds. More... | |
| void | intpol_met_4d_zeta (const met_t *met0, float height0[EX][EY][EP], float array0[EX][EY][EP], const met_t *met1, float height1[EX][EY][EP], float array1[EX][EY][EP], const double ts, const double height, const double lon, const double lat, double *var, int *ci, double *cw, const int init) |
| Interpolates meteorological variables to a given position and time. More... | |
| void | intpol_met_space_3d (const met_t *met, float array[EX][EY][EP], const double p, const double lon, const double lat, double *var, int *ci, double *cw, const int init) |
| Interpolates meteorological variables in 3D space. More... | |
| void | intpol_met_space_2d (const met_t *met, float array[EX][EY], const double lon, const double lat, double *var, int *ci, double *cw, const int init) |
| Interpolates meteorological variables in 2D space. More... | |
| void | intpol_met_time_3d (const met_t *met0, float array0[EX][EY][EP], const met_t *met1, float array1[EX][EY][EP], const double ts, const double p, const double lon, const double lat, double *var, int *ci, double *cw, const int init) |
| Interpolates meteorological data in 3D space and time. More... | |
| void | intpol_met_time_2d (const met_t *met0, float array0[EX][EY], const met_t *met1, float array1[EX][EY], const double ts, const double lon, const double lat, double *var, int *ci, double *cw, const int init) |
| Interpolates meteorological data in 2D space and time. More... | |
| void | intpol_tropo_3d (const double time0, float array0[EX][EY], const double time1, float array1[EX][EY], const double lons[EX], const double lats[EY], const int nlon, const int nlat, const double time, const double lon, const double lat, const int method, double *var, double *sigma) |
| Interpolates tropopause data in 3D (latitude, longitude, and time). More... | |
| void | jsec2time (const double jsec, int *year, int *mon, int *day, int *hour, int *min, int *sec, double *remain) |
| Converts Julian seconds to calendar date and time components. More... | |
| double | kernel_weight (const double kz[EP], const double kw[EP], const int nk, const double p) |
| Calculates the kernel weight based on altitude and given kernel data. More... | |
| double | lapse_rate (const double t, const double h2o) |
| Calculates the moist adiabatic lapse rate in Kelvin per kilometer. More... | |
| void | level_definitions (ctl_t *ctl) |
| Defines pressure levels for meteorological data. More... | |
| int | locate_irr (const double *xx, const int n, const double x) |
| Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in a sorted array. More... | |
| int | locate_irr_float (const float *xx, const int n, const double x, const int ig) |
| Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in an irregularly spaced array. More... | |
| int | locate_reg (const double *xx, const int n, const double x) |
| Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in a regular grid. More... | |
| void | locate_vert (float profiles[EX][EY][EP], const int np, const int lon_ap_ind, const int lat_ap_ind, const double alt_ap, int *ind) |
| Locate the four vertical indizes of a box for a given height value. More... | |
| void | module_advect (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Advances particle positions using different advection schemes. More... | |
| void | module_advect_init (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Initializes the advection module by setting up pressure fields. More... | |
| void | module_bound_cond (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Apply boundary conditions to particles based on meteorological and climatological data. More... | |
| void | module_chem_grid (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Computes gridded chemical tracer concentrations (volume mixing ratio) from individual air parcel mass data and assigns them back to the parcels. More... | |
| void | module_chem_init (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Initializes the chemistry modules by setting atmospheric composition. More... | |
| void | module_convection (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Performs convective mixing of atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_dd (ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm, cache_t *cache, dd_t *dd, met_t **met) |
| Manages domain decomposition and particle communication in parallel processing. More... | |
| void | module_decay (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, atm_t *atm) |
| Simulate exponential decay processes for atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_diff_meso (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Simulate mesoscale diffusion for atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_diff_pbl (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Computes particle diffusion within the planetary boundary layer (PBL). More... | |
| void | module_diff_turb (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Applies turbulent diffusion processes to atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_dry_depo (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Simulate dry deposition of atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_h2o2_chem (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Perform chemical reactions involving H2O2 within cloud particles. More... | |
| void | module_isosurf_init (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Initialize the isosurface module based on atmospheric data. More... | |
| void | module_isosurf (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Apply the isosurface module to adjust atmospheric properties. More... | |
| void | module_kpp_chem (ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| KPP chemistry module. More... | |
| void | module_meteo (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Update atmospheric properties using meteorological data. More... | |
| void | module_mixing (const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Update atmospheric properties through interparcel mixing. More... | |
| void | module_mixing_help (const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, atm_t *atm, const int *ixs, const int *iys, const int *izs, const int qnt_idx, const int use_ensemble) |
| Perform subgrid-scale interparcel mixing of a given quantity. More... | |
| void | module_oh_chem (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Perform hydroxyl chemistry calculations for atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_position (const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Update the positions and pressure levels of atmospheric particles. More... | |
| void | module_rng_init (const int ntask) |
| Initialize random number generators for parallel tasks. More... | |
| void | module_rng (const ctl_t *ctl, double *rs, const size_t n, const int method) |
| Generate random numbers using various methods and distributions. More... | |
| void | module_sedi (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Simulate sedimentation of particles in the atmosphere. More... | |
| void | module_sort (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, atm_t *atm) |
| Sort particles according to box index. More... | |
| void | module_sort_help (double *a, const int *p, const int np) |
| Reorder an array based on a given permutation. More... | |
| void | module_timesteps (const ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Calculate time steps for air parcels based on specified conditions. More... | |
| void | module_timesteps_init (ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm) |
| Initialize start time and time interval for time-stepping. More... | |
| void | module_tracer_chem (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Simulate chemical reactions involving long-lived atmospheric tracers. More... | |
| void | module_wet_depo (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm) |
| Perform wet deposition calculations for air parcels. More... | |
| void | mptrac_alloc (ctl_t **ctl, cache_t **cache, clim_t **clim, met_t **met0, met_t **met1, atm_t **atm, dd_t **dd) |
| Allocates and initializes memory resources for MPTRAC. More... | |
| void | mptrac_free (ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, clim_t *clim, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm, dd_t *dd) |
| Frees memory resources allocated for MPTRAC. More... | |
| void | mptrac_get_met (ctl_t *ctl, clim_t *clim, const double t, met_t **met0, met_t **met1, dd_t *dd) |
| Retrieves meteorological data for the specified time. More... | |
| void | mptrac_init (ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, clim_t *clim, atm_t *atm, const int ntask) |
| Initializes the MPTRAC model and its associated components. More... | |
| int | mptrac_read_atm (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm) |
| Reads air parcel data from a specified file into the given atmospheric structure. More... | |
| void | mptrac_read_clim (const ctl_t *ctl, clim_t *clim) |
| Reads various climatological data and populates the given climatology structure. More... | |
| void | mptrac_read_ctl (const char *filename, int argc, char *argv[], ctl_t *ctl) |
| Reads control parameters from a configuration file and populates the given structure. More... | |
| int | mptrac_read_met (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met, dd_t *dd) |
| Reads meteorological data from a file, supporting multiple formats and MPI broadcasting. More... | |
| void | mptrac_run_timestep (ctl_t *ctl, cache_t *cache, clim_t *clim, met_t **met0, met_t **met1, atm_t *atm, double t, dd_t *dd) |
| Executes a single timestep of the MPTRAC model simulation. More... | |
| void | mptrac_write_atm (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes air parcel data to a file in various formats. More... | |
| void | mptrac_write_met (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Writes meteorological data to a file, supporting multiple formats and compression options. More... | |
| void | mptrac_write_output (const char *dirname, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes various types of output data to files in a specified directory. More... | |
| void | mptrac_update_device (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t **met0, met_t **met1, const atm_t *atm) |
| Updates device memory for specified data structures. More... | |
| void | mptrac_update_host (const ctl_t *ctl, const cache_t *cache, const clim_t *clim, met_t **met0, met_t **met1, const atm_t *atm) |
| Updates host memory for specified data structures. More... | |
| double | nat_temperature (const double p, const double h2o, const double hno3) |
| Calculates the nitric acid trihydrate (NAT) temperature. More... | |
| double | pbl_weight (const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const int ip, const double pbl, const double ps) |
| Computes a weighting factor based on planetary boundary layer pressure. More... | |
| int | read_atm_asc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm) |
| Reads air parcel data from an ASCII file and populates the given atmospheric structure. More... | |
| int | read_atm_bin (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm) |
| Reads air parcel data from a binary file and populates the given atmospheric structure. More... | |
| int | read_atm_clams (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm) |
| Reads atmospheric data from a CLAMS NetCDF file. More... | |
| int | read_atm_nc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm) |
| Reads air parcel data from a generic netCDF file and populates the given atmospheric structure. More... | |
| void | read_clim_photo (const char *filename, clim_photo_t *photo) |
| Reads photolysis rates from a NetCDF file and populates the given photolysis structure. More... | |
| void | read_clim_photo_help (const int ncid, const char *varname, const clim_photo_t *photo, double var[CP][CSZA][CO3]) |
| Reads a 3D climatological photochemistry variable from a NetCDF file. More... | |
| int | read_clim_ts (const char *filename, clim_ts_t *ts) |
| Reads a climatological time series from a file and populates the given time series structure. More... | |
| void | read_clim_zm (const char *filename, const char *varname, clim_zm_t *zm) |
| Reads zonally averaged climatological data from a netCDF file and populates the given structure. More... | |
| void | read_kernel (const char *filename, double kz[EP], double kw[EP], int *nk) |
| Reads kernel function data from a file and populates the provided arrays. More... | |
| int | read_met_bin (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Reads meteorological data from a binary file. More... | |
| void | read_met_bin_2d (FILE *in, const met_t *met, float var[EX][EY], const char *varname) |
| Reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a binary file and stores it in the provided array. More... | |
| void | read_met_bin_3d (FILE *in, const ctl_t *ctl, const met_t *met, float var[EX][EY][EP], const char *varname, const float bound_min, const float bound_max) |
| Reads 3D meteorological data from a binary file, potentially using different compression methods. More... | |
| void | read_met_cape (const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met) |
| Calculates Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE) for each grid point. More... | |
| void | read_met_cloud (met_t *met) |
| Calculates cloud-related variables for each grid point. More... | |
| void | read_met_detrend (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Detrends meteorological data. More... | |
| void | read_met_extrapolate (met_t *met) |
| Extrapolates meteorological data. More... | |
| void | read_met_geopot (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Calculates geopotential heights from meteorological data. More... | |
| int | read_met_grib (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Reads meteorological data from a grib file and processes it. More... | |
| void | read_met_grib_grid (codes_handle **handles, int count_handles, met_t *met) |
| Reads global meteorological information from a grib file. More... | |
| void | read_met_grib_levels (codes_handle **handles, const int num_messages, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Reads meteorological variables at different vertical levels from a grib file. More... | |
| void | read_met_grib_surface (codes_handle **handles, const int num_messages, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Reads surface meteorological data from a grib file and stores it in the meteorological data structure. More... | |
| void | read_met_ml2pl (const ctl_t *ctl, const met_t *met, float var[EX][EY][EP], const char *varname) |
| Interpolates meteorological data to specified pressure levels. More... | |
| void | read_met_monotonize (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Makes zeta and pressure profiles monotone. More... | |
| int | read_met_nc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, dd_t *dd) |
| Reads meteorological data from a NetCDF file and processes it. More... | |
| void | read_met_nc_grid (const char *filename, const int ncid, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, dd_t *dd) |
| Reads meteorological grid data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition. More... | |
| void | read_met_nc_grid_dd_naive (dd_t *dd, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, const int ncid) |
| Read meteorological grid data from a NetCDF file and set up subdomain decomposition with halos. More... | |
| void | read_met_nc_levels (const int ncid, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, dd_t *dd) |
| Reads and processes meteorological level data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition. More... | |
| void | read_met_nc_surface (const int ncid, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, dd_t *dd) |
| Reads and processes surface meteorological data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition. More... | |
| int | read_met_nc_2d (const int ncid, const char *varname, const char *varname2, const char *varname3, const char *varname4, const char *varname5, const char *varname6, const ctl_t *ctl, const met_t *met, dd_t *dd, float dest[EX][EY], const float scl, const int init) |
| Reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file. More... | |
| int | read_met_nc_3d (const int ncid, const char *varname, const char *varname2, const char *varname3, const char *varname4, const ctl_t *ctl, const met_t *met, dd_t *dd, float dest[EX][EY][EP], const float scl) |
| Reads a 3-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | read_met_pbl (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Computes the planetary boundary layer (PBL) pressure based on meteorological data. More... | |
| void | read_met_periodic (met_t *met) |
| Applies periodic boundary conditions to meteorological data along longitudinal axis. More... | |
| void | read_met_polar_winds (met_t *met) |
| Applies a fix for polar winds in meteorological data. More... | |
| void | read_met_pv (met_t *met) |
| Calculates potential vorticity (PV) from meteorological data. More... | |
| void | read_met_ozone (met_t *met) |
| Calculates the total column ozone from meteorological ozone data. More... | |
| void | read_met_sample (const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Downsamples meteorological data based on specified parameters. More... | |
| void | read_met_tropo (const ctl_t *ctl, const clim_t *clim, met_t *met) |
| Calculates the tropopause and related meteorological variables based on various methods and stores the results in the meteorological data structure. More... | |
| void | read_obs (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, double *rt, double *rz, double *rlon, double *rlat, double *robs, int *nobs) |
| Reads observation data from a file and stores it in arrays. More... | |
| void | read_obs_asc (const char *filename, double *rt, double *rz, double *rlon, double *rlat, double *robs, int *nobs) |
| Reads observation data from an ASCII file. More... | |
| void | read_obs_nc (const char *filename, double *rt, double *rz, double *rlon, double *rlat, double *robs, int *nobs) |
| Reads observation data from a NetCDF file. More... | |
| double | scan_ctl (const char *filename, int argc, char *argv[], const char *varname, const int arridx, const char *defvalue, char *value) |
| Scans a control file or command-line arguments for a specified variable. More... | |
| double | sedi (const double p, const double T, const double rp, const double rhop) |
| Calculates the sedimentation velocity of a particle in air. More... | |
| void | spline (const double *x, const double *y, const int n, const double *x2, double *y2, const int n2, const int method) |
| Performs spline interpolation or linear interpolation. More... | |
| float | stddev (const float *data, const int n) |
| Calculates the standard deviation of a set of data. More... | |
| void | time2jsec (const int year, const int mon, const int day, const int hour, const int min, const int sec, const double remain, double *jsec) |
| Converts time components to seconds since January 1, 2000, 12:00:00 UTC. More... | |
| void | timer (const char *name, const char *group, const int output) |
| Measures and reports elapsed time for named and grouped timers. More... | |
| double | time_from_filename (const char *filename, const int offset) |
| Extracts and converts a timestamp from a filename to Julian seconds. More... | |
| double | tropo_weight (const clim_t *clim, const atm_t *atm, const int ip) |
| Computes a weighting factor based on tropopause pressure. More... | |
| void | write_atm_asc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes air parcel data to an ASCII file or gnuplot. More... | |
| void | write_atm_bin (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm) |
| Writes air parcel data to a binary file. More... | |
| void | write_atm_clams (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm) |
| Writes air parcel data to a NetCDF file in the CLaMS format. More... | |
| void | write_atm_clams_traj (const char *dirname, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes CLaMS trajectory data to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_atm_nc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm) |
| Writes air parcel data to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_csi (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes Critical Success Index (CSI) data to a file. More... | |
| void | write_csi_ens (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes ensemble-based Critical Success Index (CSI) and other verification statistics to an output file. More... | |
| void | write_ens (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes ensemble data to a file. More... | |
| void | write_grid (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes grid data to a file in ASCII or netCDF format. More... | |
| void | write_grid_asc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const double *cd, double *mean[NQ], double *sigma[NQ], const double *vmr_impl, const double t, const double *z, const double *lon, const double *lat, const double *area, const double dz, const int *np) |
| Writes grid data to an ASCII file. More... | |
| void | write_grid_nc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const double *cd, double *mean[NQ], double *sigma[NQ], const double *vmr_impl, const double t, const double *z, const double *lon, const double *lat, const double *area, const double dz, const int *np) |
| Writes grid data to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_met_bin (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Writes meteorological data in binary format to a specified file. More... | |
| void | write_met_bin_2d (FILE *out, met_t *met, float var[EX][EY], const char *varname) |
| Writes a 2-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file. More... | |
| void | write_met_bin_3d (FILE *out, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met, float var[EX][EY][EP], const char *varname, const int precision, const double tolerance) |
| Writes a 3-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file. More... | |
| void | write_met_nc (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met) |
| Writes meteorological data to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_met_nc_2d (const int ncid, const char *varname, met_t *met, float var[EX][EY], const float scl) |
| Writes a 2D meteorological variable to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_met_nc_3d (const int ncid, const char *varname, met_t *met, float var[EX][EY][EP], const float scl) |
| Writes a 3D meteorological variable to a NetCDF file. More... | |
| void | write_prof (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes profile data to a specified file. More... | |
| void | write_sample (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, met_t *met0, met_t *met1, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes sample data to a specified file. More... | |
| void | write_station (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes station data to a specified file. More... | |
| void | write_vtk (const char *filename, const ctl_t *ctl, const atm_t *atm, const double t) |
| Writes VTK (Visualization Toolkit) data to a specified file. More... | |
MPTRAC library declarations.
Definition in file mptrac.h.
| #define MPI_Datatype void* |
| #define codes_handle void* |
| #define CPD 1003.5 |
| #define LV 2501000. |
| #define KB 1.3806504e-23 |
| #define EP 140 |
| #define EX 1444 |
| #define NP 10000000 |
| #define NCSI 1000000 |
| #define NENS 2000 |
| #define NOBS 10000000 |
| #define CY 250 |
| #define CO3 30 |
| #define CP 70 |
| #define CSZA 50 |
| #define CT 12 |
| #define CTS 1000 |
| #define DD_NPART 100000 |
| #define DD_NNMAX 26 |
| #define DD_NPOLE -2 |
| #define DD_SPOLE -3 |
| #define ALLOC | ( | ptr, | |
| type, | |||
| n | |||
| ) |
Allocate memory for a pointer with error handling.
This macro allocates memory for a pointer of a given type and size using the calloc function. It includes error handling to check if memory allocation was successful. If the code is being compiled with OpenACC support (_OPENACC macro defined), it additionally checks if the code is running on a GPU device, and if not, it raises an error.
| ptr | Pointer variable to be allocated. |
| type | Data type of the pointer. |
| n | Number of elements to allocate memory for. |
| #define ARRAY_2D | ( | ix, | |
| iy, | |||
| ny | |||
| ) | ((ix) * (ny) + (iy)) |
Macro for computing the linear index of a 2D array element.
The ARRAY_2D macro computes the linear index of a 2D array element based on the specified row index (ix), column index (iy), and number of columns (ny).
| ix | Integer representing the row index of the 2D array element. |
| iy | Integer representing the column index of the 2D array element. |
| ny | Integer representing the number of columns in the 2D array. |
The macro computes the linear index using the formula: (ix) * (ny) + (iy). This formula assumes row-major storage, where elements of each row are stored sequentially in memory.
| #define ARRAY_3D | ( | ix, | |
| iy, | |||
| ny, | |||
| iz, | |||
| nz | |||
| ) | (((ix)*(ny) + (iy)) * (nz) + (iz)) |
Compute the linear index of a 3D array element.
This macro computes the linear index of a 3D array element based on the specified row index (ix), column index (iy), depth index (iz), number of columns (ny), and number of depths (nz).
| ix | Row index of the 3D array element. |
| iy | Column index of the 3D array element. |
| ny | Number of columns in the 3D array. |
| iz | Depth index of the 3D array element. |
| nz | Number of depths in the 3D array. |
| #define ARRHENIUS | ( | a, | |
| b, | |||
| t | |||
| ) | ((a) * exp( -(b) / (t))) |
Calculate the Arrhenius rate constant.
The Arrhenius equation is commonly used in chemical kinetics to describe the temperature dependence of reaction rates. This macro calculates the rate constant (k) based on the Arrhenius equation:
\[ k = a \times \exp( -b / T ), \]
where:
| a | Pre-exponential factor or frequency factor. |
| b | Activation energy. |
| t | Temperature in Kelvin. |
| #define CLAMP | ( | v, | |
| lo, | |||
| hi | |||
| ) | (((v) < (lo)) ? (lo) : (((v) > (hi)) ? (hi) : (v))) |
Clamp a value to a specified range.
Ensures that v lies between lo and hi. If v < lo, returns lo. If v > hi, returns hi. Otherwise, returns v unchanged.
This macro works with any numeric type (e.g., int, float, double). All arguments are evaluated exactly once — avoid passing expressions with side effects (e.g., ++ operators or function calls).
| v | Input value to clamp. |
| lo | Lower bound. |
| hi | Upper bound. |
lo and hi.Convert a longitude difference to a distance in the x-direction (east-west) at a specific latitude.
This macro calculates the distance in the x-direction (east-west) corresponding to a given longitude difference at a specific latitude using the formula:
\[ dx = dlon \times \pi \times RE / 180 times \cos(lat), \]
where:
| dlon | Difference in longitudes in degrees. |
| lat | Latitude in degrees. |
Convert a latitude difference to a distance in the y-direction (north-south).
This macro calculates the distance in the y-direction (north-south) corresponding to a given latitude difference using the formula:
\[ dy = dlat \times \pi \times RE / 180, \]
where:
| dlat | Difference in latitudes in degrees. |
| #define DEG2RAD | ( | deg | ) | ((deg) * (M_PI / 180.0)) |
Converts degrees to radians.
This macro converts an angle from degrees to radians using the formula: radians = degrees * (π / 180)
| deg | The angle in degrees to be converted. |
| #define DP2DZ | ( | dp, | |
| p | |||
| ) | (- (dp) * H0 / (p)) |
Convert a pressure difference to a height difference in the vertical direction.
This macro calculates the change in height (altitude) corresponding to a given pressure difference using the formula:
\[ dz = - (dp) \times H_0 / p \]
where:
| dp | Pressure difference in hPa. |
| p | Reference pressure in hPa. |
| #define DX2DEG | ( | dx, | |
| lat | |||
| ) |
Convert a distance in kilometers to degrees longitude at a given latitude.
This macro calculates the change in longitude in degrees corresponding to a given distance in kilometers at a specified latitude on the Earth's surface. It uses the formula:
\[ dlon = \frac{dx \times 180}{\pi \times RE \times \cos(lat)} \]
| dx | Distance in kilometers. |
| lat | Latitude in degrees. |
| #define DY2DEG | ( | dy | ) | ((dy) * 180. / (M_PI * RE)) |
Convert a distance in kilometers to degrees latitude.
This macro calculates the change in latitude in degrees corresponding to a given distance in kilometers on the Earth's surface. It uses the formula:
\[ dlat = \frac{dy \times 180}{\pi \times RE} \]
| dy | Distance in kilometers. |
| #define DZ2DP | ( | dz, | |
| p | |||
| ) | (-(dz) * (p) / H0) |
Convert a change in altitude to a change in pressure.
This macro calculates the change in pressure corresponding to a given change in altitude. It uses the hydrostatic equation:
\[ dp = -\left(dz \times \frac{p}{H_0}\right) \]
| dz | Change in altitude in kilometers. |
| p | Current pressure in hPa. |
| #define DIST | ( | a, | |
| b | |||
| ) | sqrt(DIST2(a, b)) |
Calculate the distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates.
This macro calculates the Euclidean distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates. It uses the square root of the square of the distance obtained from the DIST2 macro.
| a | Coordinates of the first point as an array of doubles. |
| b | Coordinates of the second point as an array of doubles. |
| #define DIST2 | ( | a, | |
| b | |||
| ) | ((a[0]-b[0])*(a[0]-b[0])+(a[1]-b[1])*(a[1]-b[1])+(a[2]-b[2])*(a[2]-b[2])) |
Calculate the squared Euclidean distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates.
This macro calculates the squared Euclidean distance between two points in Cartesian coordinates. It computes the sum of the squares of the differences of corresponding coordinates.
| a | Coordinates of the first point as an array of doubles. |
| b | Coordinates of the second point as an array of doubles. |
| #define DOTP | ( | a, | |
| b | |||
| ) | (a[0]*b[0]+a[1]*b[1]+a[2]*b[2]) |
Calculate the dot product of two vectors.
This macro computes the dot product of two vectors represented as arrays of doubles. It multiplies corresponding components of the vectors and sums the results.
| a | The first vector as an array of doubles. |
| b | The second vector as an array of doubles. |
| #define ECC | ( | cmd | ) |
Execute an ECCODES command and check for errors.
This macro executes an ECCODES command and checks the result. If the result indicates an error, it prints the error message using ERRMSG.
| cmd | ECCODES command to execute. |
| #define ECC_READ_2D | ( | variable, | |
| target, | |||
| scaling_factor, | |||
| found_flag | |||
| ) |
Writes 2-D data from a grib message into the meteo struct.
This macro writes 2-D data from a one-dimensional grib message into the corresponding 2-D variable in the meteo struct.
| variable | Name of the current meteorological variable |
| target | Pointer to the 2-D array in the meteo struct where the data will be stored. |
| scaling_factor | Scaling factor to apply to the data. |
| found_flag | Flag to store, that the variable was found in the grib message. |
| #define ECC_READ_3D | ( | variable, | |
| level, | |||
| target, | |||
| scaling_factor, | |||
| found_flag | |||
| ) |
Writes 3D data from a grib message into the meteo struct.
This macro writes 3D data from a one-dimensional grib message into the corresponding 3D variable in the meteo struct.
| variable | Name of the current meteorological variable. |
| level | Index of the vertical level in the 3D array where the data should be stored. |
| target | Pointer to the 3D array in the meteo struct where the data will be stored. |
| scaling_factor | Scaling factor to apply to the data. |
| found_flag | Counter to store, how many messages containing data for this variable have been read. |
| #define FMOD | ( | x, | |
| y | |||
| ) | ((x) - (int) ((x) / (y)) * (y)) |
Calculate the floating-point remainder of dividing x by y.
This macro computes the floating-point remainder of dividing x by y. It calculates this remainder as x minus the integer part of (x / y) times y.
| x | The dividend. |
| y | The divisor. |
| #define FREAD | ( | ptr, | |
| type, | |||
| size, | |||
| in | |||
| ) |
Read data from a file stream and store it in memory.
This macro reads data of a specified type from the given input file stream and stores it in the specified memory location. It ensures that the correct amount of data is read from the file stream, and if not, it raises an error.
| ptr | Pointer to the memory location where the data will be stored. |
| type | Type of the data elements to be read. |
| size | Number of elements to read. |
| in | File stream from which to read the data. |
| #define FWRITE | ( | ptr, | |
| type, | |||
| size, | |||
| out | |||
| ) |
Write data from memory to a file stream.
This macro writes data of a specified type from the specified memory location to the given output file stream. It ensures that the correct amount of data is written to the file stream, and if not, it raises an error.
| ptr | Pointer to the memory location containing the data to be written. |
| type | Type of the data elements to be written. |
| size | Number of elements to write. |
| out | File stream to which the data will be written. |
| #define INTPOL_INIT double cw[4] = {0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0}; int ci[3] = {0, 0, 0}; |
| #define INTPOL_2D | ( | var, | |
| init | |||
| ) |
Perform 2D interpolation for a meteorological variable.
This macro performs 2D interpolation for a given meteorological variable at a specific time and location.
| var | The variable to interpolate. |
| init | A flag indicating whether to initialize the interpolation arrays (cw and ci). Set to 1 for initialization, 0 otherwise. |
var.| #define INTPOL_3D | ( | var, | |
| init | |||
| ) |
Perform 3D interpolation for a meteorological variable.
This macro performs 3D interpolation for a given meteorological variable at a specific time, pressure level, and location.
| var | The variable to interpolate. |
| init | A flag indicating whether to initialize the interpolation arrays (cw and ci). Set to 1 for initialization, 0 otherwise. |
var.| #define INTPOL_SPACE_ALL | ( | p, | |
| lon, | |||
| lat | |||
| ) |
Interpolate multiple meteorological variables in space.
This macro performs spatial interpolation for multiple meteorological variables at a given pressure level, longitude, and latitude.
| p | The pressure level at which to interpolate the variables. |
| lon | The longitude at which to interpolate the variables. |
| lat | The latitude at which to interpolate the variables. |
| #define INTPOL_TIME_ALL | ( | time, | |
| p, | |||
| lon, | |||
| lat | |||
| ) |
Interpolate multiple meteorological variables in time.
This macro performs temporal interpolation for multiple meteorological variables at a given time, pressure level, longitude, and latitude.
| time | The time at which to interpolate the variables. |
| p | The pressure level at which to interpolate the variables. |
| lon | The longitude at which to interpolate the variables. |
| lat | The latitude at which to interpolate the variables. |
| #define LAPSE | ( | p1, | |
| t1, | |||
| p2, | |||
| t2 | |||
| ) |
Calculate lapse rate.
This macro calculates the lapse rate between two pressure levels given their temperatures and pressures.
| p1 | Pressure at the first level (in hPa). |
| t1 | Temperature at the first level (in K). |
| p2 | Pressure at the second level (in hPa). |
| t2 | Temperature at the second level (in K). |
| #define LIN | ( | x0, | |
| y0, | |||
| x1, | |||
| y1, | |||
| x | |||
| ) | ((y0)+((y1)-(y0))/((x1)-(x0))*((x)-(x0))) |
Linear interpolation.
This macro performs linear interpolation to estimate the value of y at a given x based on two points (x0, y0) and (x1, y1).
| x0 | X-coordinate of the first point. |
| y0 | Y-coordinate of the first point. |
| x1 | X-coordinate of the second point. |
| y1 | Y-coordinate of the second point. |
| x | The x-coordinate at which to estimate the y-value. |
| #define MAX | ( | a, | |
| b | |||
| ) | (((a)>(b))?(a):(b)) |
Macro to determine the maximum of two values.
This macro evaluates to the larger of its two arguments, a and b. It uses a ternary conditional operator to compare the values of a and b and returns a if a is greater than b; otherwise, it returns b.
| a | The first value to compare. Can be of any type that supports comparison. |
| b | The second value to compare. Can be of any type that supports comparison. |
a or b.a and b are evaluated twice. If a or b have side effects (e.g., increment operators, function calls), the side effects will occur more than once. This can lead to unexpected behavior.a and b should be of compatible types to avoid potential issues with comparison and return value.| #define MET_HEADER |
Write header for meteorological data file.
This macro writes a header to a meteorological data file, providing information about the variables stored in the file and their corresponding columns.
| out | Pointer to the file stream where the header will be written. |
| #define MIN | ( | a, | |
| b | |||
| ) | (((a)<(b))?(a):(b)) |
Macro to determine the minimum of two values.
This macro evaluates to the smaller of its two arguments, a and b. It uses a ternary conditional operator to compare the values of a and b and returns a if a is less than b; otherwise, it returns b.
| a | The first value to compare. Can be of any type that supports comparison. |
| b | The second value to compare. Can be of any type that supports comparison. |
a or b.a and b are evaluated twice. If a or b have side effects (e.g., increment operators, function calls), the side effects will occur more than once. This can lead to unexpected behavior.a and b should be of compatible types to avoid potential issues with comparison and return value.Calculate the density of a gas molecule.
This macro calculates the density of a gas molecule using the provided pressure and temperature values.
| p | Pressure of the gas in Pascals. |
| t | Temperature of the gas in Kelvin. |
| #define NC | ( | cmd | ) |
Execute a NetCDF command and check for errors.
This macro executes a NetCDF command and checks the result. If the result indicates an error, it prints the error message using ERRMSG.
| cmd | NetCDF command to execute. |
| #define NC_DEF_VAR | ( | varname, | |
| type, | |||
| ndims, | |||
| dims, | |||
| long_name, | |||
| units, | |||
| level, | |||
| quant | |||
| ) |
Define a NetCDF variable with attributes.
This macro defines a NetCDF variable with the specified name, data type, dimensions, long name, and units. It also sets the long_name and units attributes for the variable. It enables compression and quantizatio of the data.
| varname | Name of the variable. |
| type | Data type of the variable. |
| ndims | Number of dimensions for the variable. |
| dims | Array of dimension IDs. |
| long_name | Long name of the variable. |
| units | Units of the variable. |
| level | zlib compression level (0 = off). |
| quant | Number of digits for quantization (0 = off). |
nc_def_var_deflate() by nc_def_var_filter() below. Use dynamic linking, static linking does not work. Set environment variable HDF5_PLUGIN_PATH to ./libs/build/share/netcdf-plugins/.| #define NC_GET_DOUBLE | ( | varname, | |
| ptr, | |||
| force | |||
| ) |
Retrieve a double-precision variable from a NetCDF file.
This macro retrieves a double-precision variable from a NetCDF file. It first checks if the variable exists in the file and then reads its data into the specified pointer. If the force parameter is set to true, it forces the retrieval of the variable, raising an error if the variable does not exist. If force is false, it retrieves the variable if it exists and issues a warning if it does not.
| varname | Name of the variable to retrieve. |
| ptr | Pointer to the memory location where the data will be stored. |
| force | Boolean flag indicating whether to force retrieval (true) or not (false). |
| #define NC_INQ_DIM | ( | dimname, | |
| ptr, | |||
| min, | |||
| max, | |||
| check | |||
| ) |
Inquire the length of a dimension in a NetCDF file.
This macro retrieves the length of a specified dimension from a NetCDF file. It checks if the length of the dimension is within a specified range and assigns the length to the provided pointer. If the length is outside the specified range, an error message is raised.
| dimname | Name of the dimension to inquire. |
| ptr | Pointer to an integer where the dimension length will be stored. |
| min | Minimum acceptable length for the dimension. |
| max | Maximum acceptable length for the dimension. |
| check | Flag to check bounds. Set to 1 for bounds check. |
| #define NC_PUT_DOUBLE | ( | varname, | |
| ptr, | |||
| hyperslab | |||
| ) |
Write double precision data to a NetCDF variable.
This macro writes data to a specified NetCDF variable. It can handle both full variable writes and hyperslab writes depending on the hyperslab parameter. If hyperslab is true, the data is written as a hyperslab; otherwise, the entire variable is written.
| varname | Name of the NetCDF variable to write to. |
| ptr | Pointer to the data to be written. |
| hyperslab | Boolean indicating whether to write the data as a hyperslab. |
| #define NC_PUT_FLOAT | ( | varname, | |
| ptr, | |||
| hyperslab | |||
| ) |
Write a float array to a NetCDF file.
This macro writes a float array to a specified variable in a NetCDF file. Depending on the value of the hyperslab parameter, the data can be written as a hyperslab or as a whole variable.
| varname | Name of the variable to which the float array will be written. |
| ptr | Pointer to the float array to be written. |
| hyperslab | Boolean flag indicating if the data should be written as a hyperslab.
|
| #define NC_PUT_INT | ( | varname, | |
| ptr, | |||
| hyperslab | |||
| ) |
Write integer data to a NetCDF variable.
This macro writes data to a specified NetCDF variable. It can handle both full variable writes and hyperslab writes depending on the hyperslab parameter. If hyperslab is true, the data is written as a hyperslab; otherwise, the entire variable is written.
| varname | Name of the NetCDF variable to write to. |
| ptr | Pointer to the data to be written. |
| hyperslab | Boolean indicating whether to write the data as a hyperslab. |
| #define NC_PUT_ATT | ( | varname, | |
| attname, | |||
| text | |||
| ) |
Add a text attribute to a NetCDF variable.
This macro adds a text attribute to a specified NetCDF variable. It first retrieves the variable ID using its name, then it attaches the text attribute to the variable.
| varname | Name of the NetCDF variable to which the attribute will be added. |
| attname | Name of the attribute to be added. |
| text | Text of the attribute to be added. |
| #define NC_PUT_ATT_GLOBAL | ( | attname, | |
| text | |||
| ) | NC(nc_put_att_text(ncid, NC_GLOBAL, attname, strnlen(text, LEN), text)); |
Add a global text attribute to a NetCDF file.
This macro adds a text attribute to the global attributes of a NetCDF file. It directly attaches the attribute to the file, rather than to a specific variable.
| attname | Name of the global attribute to be added. |
| text | Text of the attribute to be added. |
| #define NN | ( | x0, | |
| y0, | |||
| x1, | |||
| y1, | |||
| x | |||
| ) | (fabs((x) - (x0)) <= fabs((x) - (x1)) ? (y0) : (y1)) |
Perform nearest-neighbor interpolation.
This macro returns the value of the nearest neighbor (y0 or y1) for a given x value. It compares the distances between x and x0, and between x and x1, and returns the y value corresponding to the closer x value.
| x0 | The x-coordinate of the first point. |
| y0 | The y-coordinate of the first point. |
| x1 | The x-coordinate of the second point. |
| y1 | The y-coordinate of the second point. |
| x | The x-coordinate for which the nearest neighbor is to be found. |
| #define PARTICLE_LOOP | ( | ip0, | |
| ip1, | |||
| check_dt, | |||
| ... | |||
| ) |
Loop over particle indices with OpenACC acceleration.
This macro defines a loop over particle indices from ip0 to ip1 with optional checking of dt. If _OPENACC is defined, the loop is accelerated using OpenACC directives. Otherwise, OpenMP parallelization is used.
| ip0 | The starting index of the loop (inclusive). |
| ip1 | The ending index of the loop (exclusive). |
| check_dt | Flag indicating whether to check the array dt for non-zero values. |
| ... | Optional pragma directives to be applied. |
Compute pressure at given altitude.
This macro calculates the pressure at a given altitude using the barometric formula.
| z | The altitude in kilometers. |
The barometric formula used for this calculation is:
\[ P(z) = P_0 \times e^{-(z / H_0)}, \]
where:
Compute saturation pressure over water.
This macro calculates the saturation pressure over water based on the WMO (2018) formula.
| t | The temperature in degrees Celsius. |
The saturation pressure over water is calculated using the formula:
\[ P_{\textrm{sat}}(t) = 6.112 \times e^{17.62 \times \frac{(t - T_0)}{243.12 + (t - T_0)}}, \]
where:
Compute saturation pressure over ice (WMO, 2018).
This macro calculates the saturation pressure over ice based on the WMO (2018) formula.
| t | The temperature in K. |
The saturation pressure over ice is calculated using the formula:
\[ P_{\textrm{ice}}(t) = 6.112 \times e^{22.46 \times \frac{(t - T_0)}{272.62 + (t - T_0)}}, \]
where:
Calculate partial water vapor pressure.
This macro calculates the partial water vapor pressure using the given total pressure and water vapor mixing ratio.
| p | The total pressure in hPa (hectopascals). |
| h2o | The water vapor mixing ratio in ppv (parts per volume). |
The partial water vapor pressure is calculated using the formula:
\[ P_{\textrm{w}}(p, h_2o) = \frac{p \times \max(h_2o, 0.1 \times 10^{-6})}{1 + (1 - \epsilon) \times \max(h_2o, 0.1 \times 10^{-6})}, \]
where:
| #define RAD2DEG | ( | rad | ) | ((rad) * (180.0 / M_PI)) |
Converts radians to degrees.
This macro converts an angle from radians to degrees using the formula: degrees = radians * (180 / π)
| rad | The angle in radians to be converted. |
Compute relative humidity over water.
This macro calculates the relative humidity over water using the given total pressure, temperature, and water vapor mixing ratio.
| p | The total pressure in hPa. |
| t | The temperature in K. |
| h2o | The water vapor mixing ratio in ppv (parts per volume). |
The relative humidity over water is calculated using the formula:
\[ RH_{\textrm{w}}(p, t, h_2o) = \frac{P_{\textrm{w}}(p, h_2o)}{P_{\textrm{sat}}(t)} \times 100, \]
where:
Compute relative humidity over ice.
This macro calculates the relative humidity over ice using the given total pressure, temperature, and water vapor mixing ratio.
| p | The total pressure in hPa. |
| t | The temperature in K. |
| h2o | The water vapor mixing ratio in ppv (parts per volume). |
The relative humidity over ice is calculated using the formula:
\[ RH_{\textrm{ice}}(p, t, h_2o) = \frac{P_{\textrm{w}}(p, h_2o)}{P_{\textrm{ice}}(t)} \times 100, \]
where:
| #define RHO | ( | p, | |
| t | |||
| ) | (100. * (p) / (RA * (t))) |
Compute density of air.
This macro calculates the density of air using the given total pressure and temperature.
| p | The total pressure in hPa. |
| t | The temperature in K. |
The density of air is calculated using the formula:
\[ \rho(p, t) = \frac{100 \times p}{R_a \times t}, \]
where:
| #define SET_ATM | ( | qnt, | |
| val | |||
| ) |
Set atmospheric quantity value.
This macro sets the value of a specific atmospheric quantity at a given index 'ip'. The macro first checks if the control index 'ctl->qnt' is non-negative before assigning the value, ensuring that the quantity index is valid.
| qnt | The index representing the atmospheric quantity to set. |
| val | The value to set for the atmospheric quantity. |
| #define SET_QNT | ( | qnt, | |
| name, | |||
| longname, | |||
| unit | |||
| ) |
Set atmospheric quantity index.
This macro sets the index, long name, and unit of a specific atmospheric quantity based on its name. It compares the name parameter with the name of the atmospheric quantity stored in 'ctl->qnt_name'. If a match is found, it assigns the index to 'ctl->qnt', updates the long name, and updates the unit.
| qnt | The index representing the atmospheric quantity. |
| name | The name of the atmospheric quantity. |
| longname | The long name of the atmospheric quantity. |
| unit | The unit of the atmospheric quantity. |
Compute specific humidity from water vapor volume mixing ratio.
This macro calculates the specific humidity from the water vapor volume mixing ratio. Specific humidity represents the ratio of the mass of water vapor to the total mass of air and is dimensionless.
| h2o | The water vapor volume mixing ratio. |
| #define SQR | ( | x | ) | ((x)*(x)) |
| #define SWAP | ( | x, | |
| y, | |||
| type | |||
| ) | do {type tmp = x; x = y; y = tmp;} while(0); |
| #define TDEW | ( | p, | |
| h2o | |||
| ) |
Calculate dew point temperature.
This macro computes the dew point temperature using the formula provided by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO, 2018).
| p | The atmospheric pressure in hPa. |
| h2o | The water vapor volume mixing ratio. |
Formula:
\[ T_{\textrm{dew}} = T_0 + \frac{243.12 \times \ln\left(\frac{{P_W(p, h_{2}O)}}{6.112}\right)}{17.62 - \ln\left(\frac{{P_W(p, h_{2}O)}}{6.112}\right)} \]
where:
| #define TICE | ( | p, | |
| h2o | |||
| ) |
Calculate frost point temperature (WMO, 2018).
This macro computes the frost point temperature using the formula provided by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO, 2018).
| p | The atmospheric pressure in hPa. |
| h2o | The water vapor volume mixing ratio. |
Formula:
\[ T_{\textrm{ice}} = T_0 + \frac{272.62 \times \ln\left(\frac{{P_W(p, h_{2}O)}}{6.112}\right)}{22.46 - \ln\left(\frac{{P_W(p, h_{2}O)}}{6.112}\right)} \]
where:
| #define THETA | ( | p, | |
| t | |||
| ) | ((t) * pow(1000. / (p), 0.286)) |
Compute potential temperature.
This macro calculates the potential temperature of the atmosphere.
| p | The atmospheric pressure in hPa. |
| t | The temperature in Kelvin. |
Formula:
\[ \theta = T \left( \frac{1000}{P} \right)^{0.286} \]
where:
Compute virtual potential temperature.
This macro calculates the virtual potential temperature of the atmosphere, which takes into account the effect of water vapor on the atmosphere's buoyancy.
| p | The atmospheric pressure in hPa. |
| t | The temperature in Kelvin. |
| h2o | The water vapor volume mixing ratio (ppv). |
Formula:
The virtual potential temperature ( \( \theta_v \)) is computed as
\[ \theta_v = \theta \left( 1 + \frac{0.61 \times q}{\epsilon} \right), \]
where:
| #define TOK | ( | line, | |
| tok, | |||
| format, | |||
| var | |||
| ) |
Get string tokens.
This macro extracts tokens from a given string, typically used for parsing input lines.
| line | The input string containing tokens. |
| tok | A pointer to the token string. |
| format | The format string specifying the expected format of the token. |
| var | The variable to store the parsed token value. |
The macro tokenizes the input line using space and tab characters as delimiters. It then parses each token according to the specified format string and stores the parsed value in the provided variable.
Compute virtual temperature.
This macro calculates the virtual temperature of air given its temperature and water vapor volume mixing ratio.
| t | The temperature of the air in Kelvin. |
| h2o | The water vapor volume mixing ratio. |
The virtual temperature (T_v) is computed as the temperature (t) multiplied by (1 + (1 - EPS) * max(h2o, 0.1e-6)), where EPS is the ratio of the molar mass of water vapor to the molar mass of dry air.
Convert pressure to altitude.
This macro calculates the altitude from the given pressure using the barometric formula.
| p | The pressure in hPa (hectopascal). |
Formula:
The altitude (z) is computed as H0 times the natural logarithm of the ratio of the reference pressure (P0) to the given pressure (p), where H0 is the scale height and P0 is the reference pressure at sea level.
| #define ZDIFF | ( | lnp0, | |
| t0, | |||
| h2o0, | |||
| lnp1, | |||
| t1, | |||
| h2o1 | |||
| ) |
Calculate geopotential height difference.
This macro calculates the geopotential height difference between two pressure levels using the hypsometric equation.
| lnp0 | The natural logarithm of the pressure at the first level. |
| t0 | The temperature at the first level in Kelvin (K). |
| h2o0 | The water vapor volume mixing ratio at the first level. |
| lnp1 | The natural logarithm of the pressure at the second level. |
| t1 | The temperature at the second level in Kelvin (K). |
| h2o1 | The water vapor volume mixing ratio at the second level. |
Formula: The geopotential height difference (dz) is computed as a function of the difference in natural logarithm of pressure (lnp) between the two levels, the average virtual temperature (ThetaVirt) of the two levels, the specific gas constant for dry air (RI), and the acceleration due to gravity at the surface of the Earth (G0).
| #define ZETA | ( | ps, | |
| p, | |||
| t | |||
| ) |
Computes the value of the zeta vertical coordinate.
This macro calculates the zeta vertical coordinate based on the given surface pressure (ps), pressure (p), and temperature (t). The calculation depends on the ratio p/ps:
p/ps <= 0.3, the function returns 1.0 multiplied by THETA(p, t).THETA(p, t).| ps | Surface pressure. |
| p | Pressure at the given level. |
| t | Temperature at the given level. |
| #define LOGLEV 2 |
| #define LOG | ( | level, | |
| ... | |||
| ) |
Print a log message with a specified logging level.
This macro prints a formatted log message to the standard output if the specified logging level meets certain conditions. The message will be indented if the logging level is greater than or equal to 2.
| level | The logging level of the message. This should be an integer value. |
| ... | The formatted message string and its arguments, similar to printf. |
The LOG macro provides a simple way to log messages with different levels of importance. The message is only printed if the specified level is less than or equal to the pre-defined LOGLEV macro. If the level is greater than or equal to 2, the message is preceded by two spaces for indentation.
The macro expands to a block of code that:
level is greater than or equal to 2, and if so, prints two spaces.level is less than or equal to LOGLEV, and if so, prints the formatted message followed by a newline.LOGLEV macro must be defined with an appropriate logging level before using the LOG macro.| #define WARN | ( | ... | ) |
Print a warning message with contextual information.
This macro prints a formatted warning message to the standard output, including the file name, function name, and line number where the warning occurred. The message is then passed to the LOG macro with a logging level of 0.
| ... | The formatted warning message string and its arguments, similar to printf. |
The WARN macro is used to print warning messages with additional context about where the warning was triggered. The message includes the following contextual information:
__FILE__).__func__).__LINE__).After printing this contextual information, the macro uses the LOG macro with a logging level of 0 to print the actual warning message. This ensures that warning messages are always logged, regardless of the value of LOGLEV.
LOG macro must be defined before using the WARN macro.| #define ERRMSG | ( | ... | ) |
Print an error message with contextual information and terminate the program.
This macro prints a formatted error message to the standard output, including the file name, function name, and line number where the error occurred. After printing the message, the program is terminated with an exit status indicating failure.
| ... | The formatted error message string and its arguments, similar to printf. |
The ERRMSG macro is used to report critical errors that require the program to terminate immediately. The message includes the following contextual information:
__FILE__).__func__).__LINE__).After printing this contextual information, the macro uses the LOG macro with a logging level of 0 to print the actual error message. Finally, the program exits with a failure status (EXIT_FAILURE).
LOG macro must be defined before using the ERRMSG macro.| #define PRINT | ( | format, | |
| var | |||
| ) |
Print the value of a variable with contextual information.
This macro prints the value of a variable to the standard output, including the file name, function name, and line number where the macro is called. The output also includes the variable's name and value in a formatted string.
| format | The format string used to print the variable's value, similar to printf. |
| var | The variable to be printed. |
The PRINT macro is used to output the value of a variable along with additional context about where the macro is called. The message includes:
__FILE__).__func__).__LINE__).#var).format).This macro is particularly useful for debugging purposes, providing a convenient way to trace variable values and their locations in the code.
| #define PRINT_TIMERS timer("END", "END", 1); |
Print the current state of all timers.
This macro calls the timer function with predefined arguments to signify the end of the timer logging process. It is used to print the results of all the timers that have been tracked.
timer function must be defined elsewhere in the codebase for this macro to function correctly.| #define SELECT_TIMER | ( | id, | |
| group | |||
| ) | timer(id, group, 0); |
Select and start a timer with specific attributes.
This macro stops the current timer (if any) and starts a new timer with the specified ID and group. It uses the timer function to log the timer start event.
| id | The identifier for the timer. |
| group | The group name associated with the timer. |
| void broadcast_large_data | ( | void * | data, |
| size_t | N | ||
| ) |
Broadcasts large data across all processes in an MPI communicator.
This function divides the data into manageable chunks and broadcasts each chunk sequentially. This approach is necessary because the data size may exceed the maximum allowable message size for a single MPI_Bcast operation.
| data | Pointer to the data to be broadcasted. |
| N | Size of the data in bytes. |
The function first broadcasts the total size of the data to all processes. Then, it calculates the number of chunks needed to broadcast the entire data. Each chunk is broadcasted in sequence until the entire data has been sent.
The maximum chunk size is defined as CHUNK_SIZE (2147483647 bytes).
| void cart2geo | ( | const double * | x, |
| double * | z, | ||
| double * | lon, | ||
| double * | lat | ||
| ) |
Converts Cartesian coordinates to geographic coordinates.
This function converts a point from Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) to geographic coordinates (longitude, latitude, and altitude). It uses the spherical Earth approximation for the conversion.
| x | Pointer to an array containing the Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) in kilometers. |
| z | Pointer to a double where the computed altitude (above the reference ellipsoid) will be stored, in kilometers. |
| lon | Pointer to a double where the computed longitude (in degrees) will be stored. |
| lat | Pointer to a double where the computed latitude (in degrees) will be stored. |
Converts Cartesian coordinates to geographic coordinates.
| double clim_oh | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| const double | t, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| const double | p | ||
| ) |
Calculates the hydroxyl radical (OH) concentration from climatology data, with an optional diurnal correction based on solar zenith angle.
This function retrieves OH data from a given climatology and applies a diurnal correction if the correction factor (oh_chem_beta) is greater than zero. The diurnal correction accounts for the variation in OH concentration due to changes in the solar zenith angle.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration parameters. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing OH data. |
| t | Time at which the OH concentration is to be calculated. |
| lon | Longitude at which the OH concentration is to be calculated. |
| lat | Latitude at which the OH concentration is to be calculated. |
| p | Pressure level at which the OH concentration is to be calculated. |
Definition at line 89 of file mptrac.c.
Applies a diurnal correction to the hydroxyl radical (OH) concentration in climatology data.
This function iterates over the climatology data points for OH concentration and integrates the day/night correction factor over longitude. The correction factor is based on the solar zenith angle, and it adjusts the OH data to account for diurnal variations. The corrected OH data is scaled accordingly.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration parameters, including the correction factor (oh_chem_beta). |
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing OH data that will be corrected. |
Definition at line 115 of file mptrac.c.

| double clim_photo | ( | const double | rate[CP][CSZA][CO3], |
| const clim_photo_t * | photo, | ||
| const double | p, | ||
| const double | sza, | ||
| const double | o3c | ||
| ) |
Calculates the photolysis rate for a given set of atmospheric conditions.
This function computes the photolysis rate based on provided climatology data and input parameters such as pressure, solar zenith angle (SZA), and ozone column. It ensures that the input parameters are within the valid range of the climatology data and interpolates the photolysis rate accordingly.
| rate | 3D array containing the photolysis rates for different combinations of pressure, SZA, and ozone column. |
| photo | Pointer to the climatology data structure containing arrays of valid pressure levels, SZAs, and ozone columns. |
| p | Pressure at which the photolysis rate is to be calculated. |
| sza | Solar zenith angle at which the photolysis rate is to be calculated. |
| o3c | Ozone column at which the photolysis rate is to be calculated. |
This function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 147 of file mptrac.c.
| double clim_tropo | ( | const clim_t * | clim, |
| const double | t, | ||
| const double | lat | ||
| ) |
Calculates the tropopause pressure based on climatological data.
This function computes the tropopause pressure using climatological data for different times and latitudes. It interpolates the tropopause pressure based on the input time and latitude parameters.
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing tropopause pressure data. |
| t | Time for which the tropopause pressure is to be calculated, in seconds since the beginning of the year. |
| lat | Latitude at which the tropopause pressure is to be calculated. |
This function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 204 of file mptrac.c.
| void clim_tropo_init | ( | clim_t * | clim | ) |
Initializes the tropopause data in the climatology structure.
This function initializes the tropopause data in the climatology structure. It sets the time steps, latitudes, and tropopause pressure values based on predefined arrays.
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure to be initialized. |
This function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 232 of file mptrac.c.
| double clim_ts | ( | const clim_ts_t * | ts, |
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Interpolates a time series of climatological variables.
This function interpolates a time series of climatological variables based on the input time and the provided data points.
| ts | Pointer to the time series structure containing data points. |
| t | Time at which to interpolate the climatological variable (in seconds). |
This function performs linear interpolation between the closest data points to the input time t. If t is outside the range of the provided time series, the value at the nearest boundary is returned.
Definition at line 387 of file mptrac.c.

| double clim_zm | ( | const clim_zm_t * | zm, |
| const double | t, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| const double | p | ||
| ) |
Interpolates monthly mean zonal mean climatological variables.
This function interpolates climatological variables based on pressure, latitude, and time. The climatological data is provided in the form of monthly mean zonal mean values.
| zm | Pointer to the climatological zonal mean structure containing data points. |
| t | Time at which to interpolate the climatological variable (in seconds since the beginning of the year). |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate the climatological variable (in degrees). |
| p | Pressure at which to interpolate the climatological variable (in hPa). |
This function performs trilinear interpolation between the nearest data points to the input time t, latitude lat, and pressure or altitude p. If the input values are outside the range of the provided data, the function extrapolates by using the nearest boundary values.
Definition at line 405 of file mptrac.c.
| void compress_cms | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| float * | array, | ||
| const size_t | nx, | ||
| const size_t | ny, | ||
| const size_t | np, | ||
| const double * | plev, | ||
| const int | decompress, | ||
| FILE * | inout | ||
| ) |
Compresses or decompresses a 3-D meteorological field using cmultiscale.
This routine operates on a longitude/latitude regular grid of size nx × ny and np vertical levels. The grid coordinates are generated internally:
nx pointsny pointsIf decompress is non-zero, the function reads np CMS solutions from inout (optionally using Zstd), evaluates them on the lon/lat grid, and fills array (3-D layout via ARRAY_3D macro).
If decompress is zero, the function processes the input array level-by-level:
varname (e.g., "T","U","V",...)inout (optionally using Zstd)The overall compression ratio reported in logs is the harmonic mean across levels.
| [in] | ctl | Control/settings structure providing CMS parameters (Nd0, max level, eps per variable, batching, and whether to use Zstd for I/O). |
| [in] | varname | Variable name used for selecting the CMS epsilon threshold (case-insensitive). Supported names include: "Z","T","U","V","W","PV","H2O","O3","LWC","RWC","IWC","SWC","CC". |
| [in,out] | array | Field data buffer.
|
| [in] | nx | Number of longitude grid points (must be >= 2). |
| [in] | ny | Number of latitude grid points (must be >= 2). |
| [in] | np | Number of vertical levels (pressure levels). |
| [in] | plev | Pressure levels array of length np (used for logging). |
| [in] | decompress | If non-zero, read CMS stream from inout and reconstruct array. If zero, build CMS solutions from array and write them to inout. |
| [in,out] | inout | Binary stream used for CMS I/O:
|
varname must match one of the supported variable names; otherwise an error is raised.| void compress_pck | ( | const char * | varname, |
| float * | array, | ||
| const size_t | nxy, | ||
| const size_t | nz, | ||
| const int | decompress, | ||
| FILE * | inout | ||
| ) |
Compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats.
This function either compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats based on the value of the decompress parameter. Compression reduces the storage size by converting float values (4 bytes) to unsigned short values (2 bytes) with scaling and offset. Decompression restores the original float values from the compressed unsigned short representation.
| varname | The name of the variable being processed. |
| array | Pointer to the 3D array of floats to be compressed or decompressed. |
| nxy | The number of elements in the first two dimensions of the array. |
| nz | The number of elements in the third dimension of the array. |
| decompress | If non-zero, the function will decompress the data; otherwise, it will compress the data. |
| inout | File pointer for input or output operations. It is used for reading compressed data during decompression and writing compressed data during compression. |
The function performs the following steps:
array.The function allocates memory for the compressed data array and frees it before returning.
Definition at line 680 of file mptrac.c.
| void compress_sz3 | ( | const char * | varname, |
| float * | array, | ||
| const int | nx, | ||
| const int | ny, | ||
| const int | nz, | ||
| const int | precision, | ||
| const double | tolerance, | ||
| const int | decompress, | ||
| FILE * | inout | ||
| ) |
Compresses or decompresses a 3-D float array using the SZ3 library.
This function either compresses a 3-D floating-point array and writes it to a file stream, or reads compressed SZ3 data from a file stream and decompresses it into the provided array. The SZ3 error bound can be specified either by relative precision (bits) or absolute tolerance.
| varname | Name of the variable (used for logging). |
| array | Pointer to the 3-D float array (input for compression, output for decompression). |
| nx | Size of the first dimension. |
| ny | Size of the second dimension. |
| nz | Size of the third dimension. |
| precision | Relative precision in bits (used if > 0; tolerance must be 0). |
| tolerance | Absolute error bound (used if > 0; precision must be 0). |
| decompress | Non-zero to decompress data from inout into array; zero to compress array into inout. |
| inout | File stream for reading/writing compressed data. |
precision or tolerance must be set to a positive value. SZ_FLOAT for this function.| ERRMSG | if input parameters are invalid, memory allocation fails, compression/decompression fails, or file I/O errors occur. |
| void compress_zfp | ( | const char * | varname, |
| float * | array, | ||
| const int | nx, | ||
| const int | ny, | ||
| const int | nz, | ||
| const int | precision, | ||
| const double | tolerance, | ||
| const int | decompress, | ||
| FILE * | inout | ||
| ) |
Compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats using the ZFP library.
This function either compresses or decompresses a 3D array of floats based on the value of the decompress parameter. Compression reduces the storage size using the ZFP compression algorithm, which supports fixed-precision or fixed-accuracy modes. Decompression restores the original float values from the compressed representation.
| varname | The name of the variable being processed. |
| array | Pointer to the 3D array of floats to be compressed or decompressed. |
| nx | The number of elements in the x-dimension of the array. |
| ny | The number of elements in the y-dimension of the array. |
| nz | The number of elements in the z-dimension of the array. |
| precision | The precision parameter for ZFP compression. If greater than 0, it sets the fixed precision mode. |
| tolerance | The tolerance parameter for ZFP compression. If greater than 0 and precision is 0, it sets the fixed accuracy mode. |
| decompress | If non-zero, the function will decompress the data; otherwise, it will compress the data. |
| inout | File pointer for input or output operations. It is used for reading compressed data during decompression and writing compressed data during compression. |
The function performs the following steps:
array.The function logs the compression or decompression details and frees allocated resources before returning.
| void compress_zstd | ( | const char * | varname, |
| float * | array, | ||
| const size_t | n, | ||
| const int | decompress, | ||
| const int | level, | ||
| FILE * | inout | ||
| ) |
Compresses or decompresses a float array using Zstandard (ZSTD).
This function either compresses a given float array and writes the result to a file, or reads compressed data from a file and decompresses it into the array.
| [in] | varname | Name of the variable, used for logging. |
| [in,out] | array | Pointer to the float array to compress or to fill with decompressed data. |
| [in] | n | Number of float elements in the array. |
| [in] | decompress | If non-zero, perform decompression; otherwise, perform compression. |
| [in] | level | Compression level (-5 to 22). Use 0 for the ZSTD default. |
| [in,out] | inout | File pointer for input/output. Used for reading or writing compressed data. |
array has sufficient space for uncompressed data.| double cos_sza | ( | const double | sec, |
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat | ||
| ) |
Calculates the cosine of the solar zenith angle.
This function computes the cosine of the solar zenith angle (SZA), which describes the angle between the local zenith (straight up) and the line connecting the observer to the center of the Sun. The cosine of the SZA is often used directly in radiative transfer and photochemical calculations to avoid unnecessary use of trigonometric inverse functions.
| sec | Seconds elapsed since 2000-01-01T12:00Z. |
| lon | Observer's longitude in degrees. |
| lat | Observer's latitude in degrees. |
The cosine of the solar zenith angle is computed based on the observer's position (longitude and latitude) and the specified time in seconds elapsed since 2000-01-01T12:00Z.
Definition at line 1011 of file mptrac.c.
| void day2doy | ( | const int | year, |
| const int | mon, | ||
| const int | day, | ||
| int * | doy | ||
| ) |
Get day of year from date.
Converts a given date to the day of the year (DOY).
This function computes the day of the year (DOY) for a given date specified by the year, month, and day. It takes into account whether the given year is a leap year or not.
| year | The year of the date. |
| mon | The month of the date (1-12). |
| day | The day of the month (1-31). |
| doy | Pointer to an integer where the computed day of the year will be stored. |
The function uses two arrays, d0 and d0l, which contain the cumulative number of days at the start of each month for non-leap years and leap years respectively. It checks if the year is a leap year and calculates the day of the year accordingly.
Definition at line 1052 of file mptrac.c.
Assign atmospheric particles to rectangular subdomains.
This function classifies particles in an atmospheric model into subdomains defined by the domain decomposition (dd). Depending on whether this is the initial assignment (init != 0) or a subsequent reclassification, it either:
Longitude values are wrapped into the [0, 360) range to ensure consistency, and boundary conditions at the left and right edges of the domain are handled explicitly. Particles falling outside the subdomain bounds are marked with -1 during initialization.
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to an atm_t structure containing particle data:
|
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters, including subdomain indices and query IDs (e.g., ctl->qnt_subdomain). |
| [in] | dd | Pointer to a dd_t structure containing decomposition information:
|
| [in] | init | Flag indicating whether this is the initial assignment (init != 0) or a reclassification (init == 0). |
_OPENACC.dd->neighbours follow a directional convention (left, right, up, down, and diagonals).-1 during initialization.| void dd_atm2particles | ( | atm_t * | atm, |
| particle_t * | particles, | ||
| ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| int * | nparticles, | ||
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| int | rank | ||
| ) |
Extracts particles from an atmospheric state and prepares them for inter-domain transfer.
This routine scans the atmospheric arrays for particles that should be transferred to another MPI/OpenMP/OpenACC rank (i.e., particles whose destination subdomain differs from the current rank). For each such particle, the function copies its prognostic variables (time, position, pressure, tracers) into the particles buffer and marks the particle in the atmospheric fields as inactive by setting its subdomain flag to -1.
Additionally, the particle's timestep entry in cache is reset so that the receiving process can re-initialize it.
If compiled with OpenACC, the function also manages the corresponding device data movement for particles and nparticles, and performs the selection loop on the accelerator.
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric state. Particle properties (time, lon, lat, pressure, tracer fields) are read from this structure. The particle’s subdomain field is overwritten and set to -1 for particles selected for transfer. |
| [out] | particles | Output buffer where selected particles are copied. The array must be allocated to hold at least *nparticles entries. Indexing is relative to atm->np. |
| [in] | ctl | Model control structure containing metadata such as the number of tracers (ctl->nq), and indices of relevant tracer fields (ctl->qnt_destination, ctl->qnt_subdomain). |
| [in,out] | nparticles | On input, the number of particles to inspect (particles with indices [atm->np, atm->np + *nparticles)). On output, unchanged. Device copies may be created or updated when using OpenACC. |
| [in,out] | cache | Cache structure used to store per-particle timestep values. For each particle selected for transfer, cache->dt[ip] is set to 0. |
| [in] | rank | Rank of the current processing unit. Particles whose destination field does not match rank are selected for transfer. |
atm->q[ctl->qnt_destination][ip] != rank| int dd_calc_subdomain_from_coords | ( | double | lon, |
| double | lat, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| int | mpi_size, | ||
| int | nx_glob, | ||
| int | ny_glob | ||
| ) |
Computes the destination subdomain (MPI rank) for a particle based on its geographic coordinates.
This function determines which distributed-memory subdomain a particle belongs to, given its longitude and latitude. It performs several steps:
met).The rank is finally clamped into the valid range [0, mpi_size-1].
| [in] | lon | Input longitude in degrees. May lie outside [0, 360). Values are wrapped. |
| [in] | lat | Input latitude in degrees. May lie outside the range [−90, 90]. Values past the poles are wrapped and the longitude is flipped accordingly. |
| [in] | met | Pointer to meteorological grid information. Only the longitude and latitude arrays (met->lon[], met->lat[]) are used to determine the global range of coordinates. |
| [in] | ctl | Model control structure. Provides the number of zonal and meridional subdomains (ctl->dd_subdomains_zonal, ctl->dd_subdomains_meridional) used for domain decomposition. |
| [in] | mpi_size | Number of MPI ranks participating in the simulation. The computed target rank is clamped to [0, mpi_size - 1]. |
| [in] | nx_glob | Number of global longitude points in met->lon. Used to compute the global longitude range. |
| [in] | ny_glob | Number of global latitude points in met->lat. Used to compute the global latitude range. |
[0, mpi_size - 1].| void dd_communicate_particles | ( | particle_t * | particles, |
| int * | nparticles, | ||
| MPI_Datatype | MPI_Particle, | ||
| int * | neighbours, | ||
| int | nneighbours, | ||
| ctl_t | ctl | ||
| ) |
Communicates particles between MPI processes.
The dd_communicate_particles function manages the communication of particle data between neighbouring MPI processes. It sends and receives particles to and from neighbouring ranks, handling the allocation and deallocation of buffers, and ensuring proper synchronization.
| particles | An array of particle_t structures to be communicated. |
| nparticles | A pointer to an integer representing the number of particles. |
| MPI_Particle | An MPI_Datatype representing the structure of a particle. |
| neighbours | An array of integers representing the neighbouring ranks. |
| nneighbours | An integer representing the number of neighbours. |
| ctl | A control structure (ctl_t) containing configuration parameters. |
The function performs the following steps:
particles array and other parameters are properly initialized. It handles communication with neighbouring ranks, ignoring poles and empty signals. The function uses MPI non-blocking communication for efficiency.Determines rectangular neighbouring ranks for MPI processes.
The dd_get_rect_neighbour function calculates and assigns the neighbouring ranks for an MPI process based on its current rank and the configuration of subdomains. This is typically used in parallel computing to manage data decomposition and communication between processes arranged in a rectangular grid.
| ctl | A control structure (ctl_t) containing configuration parameters for subdomains. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure where neighbour information will be stored. |
The function performs the following steps:
neighbours array in the dd structure.ctl and dd structures are properly initialized. The function considers different configurations for processes at the boundaries and handles them appropriately to ensure correct neighbour assignment.Initializes domain decomposition for parallel processing.
The dd_init function initializes the domain decomposition setup for parallel processing in a distributed computing environment. It ensures that the number of tasks matches the number of subdomains, registers a custom MPI datatype for particle structures, defines grid neighbours, and assigns particles to their respective subdomains.
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
The function performs the following steps:
dd_register_MPI_type_particle.dd_get_rect_neighbour.dd_assign_rect_subdomains_atm.ctl, dd, atm, and met structures are properly initialized. The function is typically called at the beginning of a parallel processing task to set up the environment.| int dd_is_periodic_longitude | ( | met_t * | met, |
| int | nx_glob | ||
| ) |
Check whether the longitude grid is periodic (global coverage).
This function determines if the longitude array in met represents a global, periodic grid (covering 360°). It does so by computing the longitude spacing and testing whether the total range of longitudes plus one spacing approximately equals 360 degrees.
| [in] | met | Pointer to a met_t structure containing the longitude array (met->lon). |
| [in] | nx_glob | Number of global longitude grid points. |
| 1 | The longitude grid is periodic (global). |
| 0 | The longitude grid is not periodic (regional). |
read_met_periodic().| void dd_particles2atm | ( | atm_t * | atm, |
| particle_t * | particles, | ||
| ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| int * | nparticles, | ||
| cache_t * | cache | ||
| ) |
Converts particle data to atmospheric data.
The dd_particles2atm function converts data from an array of particle structures (particle_t) to an atmospheric data structure (atm_t). It updates the atmospheric data with values from the particles and modifies the cache with control parameters (ctl_t).
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data to be updated. |
| particles | An array of particle_t structures from which data will be taken. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| nparticles | A pointer to an integer representing the number of particles to process. |
| cache | A pointer to a cache_t structure used for storing intermediate values. |
The function performs the following steps:
particles array and atm structure are properly initialized. It also assumes that the cache is pre-allocated and accessible. The function uses OpenACC directives for parallel processing.| void dd_register_MPI_type_particle | ( | MPI_Datatype * | MPI_Particle | ) |
Registers a custom MPI datatype for particle structures.
The dd_register_MPI_type_particle function creates and commits a custom MPI datatype that represents the structure of a particle (particle_t). This datatype is used for efficient communication of particle data in MPI operations.
| MPI_Particle | A pointer to an MPI_Datatype variable where the new datatype will be stored. |
The function performs the following steps:
offsetof macro.MPI_Type_create_struct.MPI_Type_commit.particle_t structure is defined and accessible. The NQ constant should be defined to represent the number of quantities in the particle structure.| void dd_sort | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| dd_t * | dd, | ||
| int * | nparticles, | ||
| int * | rank | ||
| ) |
Sort particles according to box index and target rank for neighbours.
The dd_sort function sorts particles within the atmospheric data structure (atm_t) based on their geographical coordinates (longitude and latitude) and pressure level. It also considers the target rank to which a particle will be sent. The function allocates temporary arrays to store indices and auxiliary data for sorting, then performs the sorting operation. After sorting, it updates the order of particles in the atmospheric data structure.
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters and settings. |
| met0 | A pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data at the current time step. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data with particle information. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
| nparticles | A pointer to an integer representing the number of particles to be sent. |
| rank | A pointer to an integer storing the current MPI rank. |
The function performs the following steps:
ctl, met0, atm, nparticles, and rank parameters are properly initialized. locate_reg and locate_irr functions to determine the appropriate index for sorting particles. | void dd_sort_help | ( | double * | a, |
| dd_t * | dd, | ||
| const int | np | ||
| ) |
Reorder an array according to a permutation vector.
This function reorders the contents of the array a using the permutation indices stored in dd->p. A temporary buffer (dd->help) is used to perform the reordering in two passes:
a are copied into dd->help in permuted order.dd->help is copied back into a in sequential order.Parallelization is supported with OpenACC or OpenMP, depending on compilation flags.
| [in,out] | a | Pointer to the array of doubles to be reordered. On input, it contains the original data; on output, it contains the reordered data. |
| [in,out] | dd | Pointer to a dd_t structure containing:
|
| [in] | np | Number of elements in the array and permutation vector. |
dd->p and dd->help arrays must be allocated with at least np elements.#pragma acc when compiled with OpenACC (_OPENACC defined), otherwise falls back to OpenMP.| void doy2day | ( | const int | year, |
| const int | doy, | ||
| int * | mon, | ||
| int * | day | ||
| ) |
Converts a given day of the year (DOY) to a date (month and day).
This function computes the month and day for a given day of the year (DOY) and year. It accounts for whether the given year is a leap year or not.
| year | The year corresponding to the DOY. |
| doy | The day of the year (1-365 or 1-366). |
| mon | Pointer to an integer where the computed month will be stored. |
| day | Pointer to an integer where the computed day of the month will be stored. |
The function uses two arrays, d0 and d0l, which contain the cumulative number of days at the start of each month for non-leap years and leap years respectively. It checks if the year is a leap year and calculates the month and day of the month accordingly.
Definition at line 1893 of file mptrac.c.
| void fft_help | ( | double * | fcReal, |
| double * | fcImag, | ||
| const int | n | ||
| ) |
Computes the Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) of a complex sequence.
This function calculates the FFT of a complex sequence represented by separate arrays for the real and imaginary parts. The input arrays fcReal and fcImag are modified in place to contain the transformed data.
| fcReal | Pointer to an array of doubles representing the real part of the input sequence. The array should have at least n elements. |
| fcImag | Pointer to an array of doubles representing the imaginary part of the input sequence. The array should have at least n elements. |
| n | The number of complex data points in the input sequence. This value should not exceed PMAX. |
fcReal and fcImag must point to arrays of at least n elements. n must be less than or equal to PMAX.fcReal and fcImag will contain the real and imaginary parts of the FFT result, respectively.n exceeds PMAX, the function will trigger an error message and terminate.Definition at line 1923 of file mptrac.c.
| void geo2cart | ( | const double | z, |
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | x | ||
| ) |
Converts geographic coordinates (longitude, latitude, altitude) to Cartesian coordinates.
This function converts geographic coordinates specified by longitude, latitude, and altitude into Cartesian coordinates. The Earth is approximated as a sphere with radius defined by the constant RE.
| z | The altitude above the Earth's surface in kilometers. |
| lon | The longitude in degrees. |
| lat | The latitude in degrees. |
| x | Pointer to an array of three doubles where the computed Cartesian coordinates (x, y, z) will be stored. |
The function computes the Cartesian coordinates using the given altitude, longitude, and latitude. It assumes the Earth is a perfect sphere and uses the following formulas:
RE is defined as the Earth's radius in kilometers. | void get_met_help | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const double | t, | ||
| const int | direct, | ||
| const char * | metbase, | ||
| const double | dt_met, | ||
| char * | filename | ||
| ) |
Generates a formatted filename for meteorological data files based on the input parameters.
This function determines a rounded time interval, decodes the time components (year, month, day, hour, minute, second), and constructs a filename string for meteorological data files in various formats. The filename is adjusted based on the input control settings.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration settings. |
| [in] | t | The time value in seconds since a reference epoch. |
| [in] | direct | Direction to round the time value. Use -1 for rounding down and 1 for rounding up. |
| [in] | metbase | Base string for the filename, representing the dataset. |
| [in] | dt_met | Time interval for rounding in seconds. |
| [out] | filename | Output buffer to store the generated filename. |
Definition at line 1980 of file mptrac.c.
| void get_met_replace | ( | char * | orig, |
| char * | search, | ||
| char * | repl | ||
| ) |
Replaces occurrences of a substring in a string with another substring.
This function replaces occurrences of the substring search in the string orig with the substring repl. The replacement is performed in-place.
| orig | The original string where replacements are to be made. |
| search | The substring to be replaced. |
| repl | The substring to replace occurrences of search. |
The function iterates over the original string orig and replaces each occurrence of the substring search with the substring repl. It performs the replacement operation up to three times to ensure multiple occurrences are replaced.
YYYY, MM, and DD by year, month, and day in filenames. orig, search, and repl are properly initialized and have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2047 of file mptrac.c.
| void get_tropo | ( | const int | met_tropo, |
| ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| const double * | lons, | ||
| const int | nx, | ||
| const double * | lats, | ||
| const int | ny, | ||
| double * | pt, | ||
| double * | zt, | ||
| double * | tt, | ||
| double * | qt, | ||
| double * | o3t, | ||
| double * | ps, | ||
| double * | zs | ||
| ) |
Calculate tropopause data.
This function reads and interpolates various meteorological parameters such as tropopause pressure, temperature, and ozone concentration at specified latitudes and longitudes. The interpolated data is stored in the provided arrays.
| met_tropo | An integer specifying the type of meteorological data to use. |
| ctl | Pointer to a ctl_t structure that controls the meteorological data processing. |
| clim | Pointer to a clim_t structure containing climatological data. |
| met | Pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data. |
| lons | Array of longitudes at which to interpolate data. The array should have nx elements. |
| nx | Number of longitude points. |
| lats | Array of latitudes at which to interpolate data. The array should have ny elements. |
| ny | Number of latitude points. |
| pt | Pointer to an array where the interpolated pressure values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| zt | Pointer to an array where the interpolated height values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| tt | Pointer to an array where the interpolated temperature values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| qt | Pointer to an array where the interpolated specific humidity values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| o3t | Pointer to an array where the interpolated ozone concentration values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| ps | Pointer to an array where the interpolated surface pressure values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
| zs | Pointer to an array where the interpolated surface height values will be stored. The array should have nx * ny elements. |
lons must have at least nx elements. lats must have at least ny elements. pt, zt, tt, qt, o3t, ps, and zs must have at least nx * ny elements.pt, zt, tt, qt, o3t, ps, and zs will contain the interpolated meteorological data.read_met_tropo, intpol_met_space_2d, and intpol_met_space_3d for reading and interpolating the tropopause data.Definition at line 2071 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_check_lon_lat | ( | const double * | lons, |
| const int | nlon, | ||
| const double * | lats, | ||
| const int | nlat, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | lon2, | ||
| double * | lat2 | ||
| ) |
Adjusts longitude and latitude to ensure they fall within valid bounds.
This function checks and modifies the given longitude and latitude values to fit within the specified longitude and latitude arrays. The longitude is wrapped within a 360-degree range, and the latitude is clamped within the valid range defined by the latitude array.
| [in] | lons | Pointer to an array of valid longitude values. |
| [in] | nlon | Number of elements in the longitude array. |
| [in] | lats | Pointer to an array of valid latitude values. |
| [in] | nlat | Number of elements in the latitude array. |
| [in] | lon | Input longitude to be checked and adjusted. |
| [in] | lat | Input latitude to be checked and adjusted. |
| [out] | lon2 | Pointer to the adjusted longitude. |
| [out] | lat2 | Pointer to the adjusted latitude. |
Definition at line 2114 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_met_4d_zeta | ( | const met_t * | met0, |
| float | height0[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| float | array0[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const met_t * | met1, | ||
| float | height1[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| float | array1[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const double | ts, | ||
| const double | height, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| int * | ci, | ||
| double * | cw, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological variables to a given position and time.
This function interpolates meteorological variables to a specified position and time. It calculates the interpolated value based on the values provided at two time steps and performs interpolation in time, longitude, latitude, and altitude dimensions.
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the first time step. |
| height0 | Array containing heights at the first time step. |
| array0 | Array containing meteorological variable values at the first time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the second time step. |
| height1 | Array containing heights at the second time step. |
| array1 | Array containing meteorological variable values at the second time step. |
| ts | Interpolation time (fractional time between met0 and met1). |
| height | Altitude at which to interpolate. |
| lon | Longitude at which to interpolate. |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate. |
| var | Pointer to store the interpolated variable value. |
| ci | Array to store the calculated indices. |
| cw | Array to store the weighting factors. |
| init | Flag indicating if it's the first call (1) or not (0). |
The function first restricts the longitude within the range [0, 360) degrees. It then calculates the horizontal indices (ci[0] and ci[1]) based on the provided longitude and latitude. Next, it locates the vertical indices for each edge of the column based on the provided height.
The function then calculates the weighting factors for time, longitude, latitude, and altitude. It iterates over the interpolation process to determine the altitude weighting factor. After initializing the interpolation parameters, it calculates the interpolated variable value and stores it in the memory location pointed to by var.
height0, array0, height1, array1, ci, cw) have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2141 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_met_space_3d | ( | const met_t * | met, |
| float | array[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const double | p, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| int * | ci, | ||
| double * | cw, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological variables in 3D space.
This function interpolates meteorological variables at a specified pressure level and geographic position. It calculates the interpolated value based on the values provided at neighboring grid points and performs interpolation in pressure, longitude, and latitude dimensions.
| met | Pointer to the meteorological data. |
| array | Array containing meteorological variable values. |
| p | Pressure level at which to interpolate. |
| lon | Longitude at which to interpolate. |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate. |
| var | Pointer to store the interpolated variable value. |
| ci | Array to store the calculated indices. |
| cw | Array to store the weighting factors. |
| init | Flag indicating if it's the first call (1) or not (0). |
The function first checks the longitude and adjusts it if necessary to ensure it falls within the valid range. It then calculates the interpolation indices based on the provided pressure level, longitude, and latitude. Next, it computes the interpolation weights for pressure, longitude, and latitude.
The function interpolates vertically first and then horizontally. The interpolated value is stored in the memory location pointed to by var.
array, ci, and cw arrays have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2313 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_met_space_2d | ( | const met_t * | met, |
| float | array[EX][EY], | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| int * | ci, | ||
| double * | cw, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological variables in 2D space.
This function interpolates meteorological variables at a specified geographic position. It calculates the interpolated value based on the values provided at neighboring grid points and performs interpolation in longitude and latitude dimensions.
| met | Pointer to the meteorological data. |
| array | Array containing meteorological variable values. |
| lon | Longitude at which to interpolate. |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate. |
| var | Pointer to store the interpolated variable value. |
| ci | Array to store the calculated indices. |
| cw | Array to store the weighting factors. |
| init | Flag indicating if it's the first call (1) or not (0). |
The function first checks the longitude and adjusts it if necessary to ensure it falls within the valid range. It then calculates the interpolation indices based on the provided longitude and latitude. Next, it computes the interpolation weights for longitude and latitude.
The function interpolates horizontally and stores the interpolated value in the memory location pointed to by var. If any of the data values used in interpolation are not finite, the function handles this situation by choosing a valid value or performing a simple interpolation.
array, ci, and cw arrays have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2371 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_met_time_3d | ( | const met_t * | met0, |
| float | array0[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const met_t * | met1, | ||
| float | array1[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const double | ts, | ||
| const double | p, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| int * | ci, | ||
| double * | cw, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological data in 3D space and time.
This function interpolates meteorological data in three dimensions (longitude, latitude, and pressure) and time. It calculates the interpolated value based on the values provided at neighboring grid points and performs interpolation both spatially and temporally.
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at time t0. |
| array0 | 3D array of meteorological data at time t0. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at time t1. |
| array1 | 3D array of meteorological data at time t1. |
| ts | Time stamp at which to interpolate. |
| p | Pressure level at which to interpolate. |
| lon | Longitude at which to interpolate. |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate. |
| var | Pointer to store the interpolated value. |
| ci | Array to store the calculated indices. |
| cw | Array to store the weighting factors. |
| init | Flag indicating if it's the first call (1) or not (0). |
The function first performs spatial interpolation for both time instances (t0 and t1) using the intpol_met_space_3d function. It then calculates the weighting factor wt based on the time stamp ts. Finally, it performs temporal interpolation using the interpolated values at t0 and t1 along with the weighting factor to compute the final interpolated value stored in var.
ci and cw arrays have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2429 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_met_time_2d | ( | const met_t * | met0, |
| float | array0[EX][EY], | ||
| const met_t * | met1, | ||
| float | array1[EX][EY], | ||
| const double | ts, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| int * | ci, | ||
| double * | cw, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological data in 2D space and time.
This function interpolates meteorological data in two dimensions (longitude and latitude) and time. It calculates the interpolated value based on the values provided at neighboring grid points and performs interpolation both spatially and temporally.
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at time t0. |
| array0 | 2D array of meteorological data at time t0. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at time t1. |
| array1 | 2D array of meteorological data at time t1. |
| ts | Time stamp at which to interpolate. |
| lon | Longitude at which to interpolate. |
| lat | Latitude at which to interpolate. |
| var | Pointer to store the interpolated value. |
| ci | Array to store the calculated indices. |
| cw | Array to store the weighting factors. |
| init | Flag indicating if it's the first call (1) or not (0). |
The function first performs spatial interpolation for both time instances (t0 and t1) using the intpol_met_space_2d function. It then calculates the weighting factor wt based on the time stamp ts. Finally, it performs temporal interpolation using the interpolated values at t0 and t1 along with the weighting factor to compute the final interpolated value stored in var. If one of the interpolated values is not finite, it selects the valid value based on the weighting factor wt.
ci and cw arrays have sufficient memory allocated before calling this function.Definition at line 2458 of file mptrac.c.
| void intpol_tropo_3d | ( | const double | time0, |
| float | array0[EX][EY], | ||
| const double | time1, | ||
| float | array1[EX][EY], | ||
| const double | lons[EX], | ||
| const double | lats[EY], | ||
| const int | nlon, | ||
| const int | nlat, | ||
| const double | time, | ||
| const double | lon, | ||
| const double | lat, | ||
| const int | method, | ||
| double * | var, | ||
| double * | sigma | ||
| ) |
Interpolates tropopause data in 3D (latitude, longitude, and time).
This function performs interpolation of tropopause data at a given latitude, longitude, and time. The interpolation can be performed using either linear interpolation or nearest neighbor interpolation. The standard deviation of the data points used in the interpolation is also computed.
| time0 | Time corresponding to the first data array array0. |
| array0 | A 2D array of tropopause data at time0. The dimensions are EX by EY. |
| time1 | Time corresponding to the second data array array1. |
| array1 | A 2D array of tropopause data at time1. The dimensions are EX by EY. |
| lons | Array of longitudes with EX elements. |
| lats | Array of latitudes with EY elements. |
| nlon | Number of longitudes. |
| nlat | Number of latitudes. |
| time | The specific time at which to interpolate the data. |
| lon | The specific longitude at which to interpolate the data. |
| lat | The specific latitude at which to interpolate the data. |
| method | Interpolation method: 1 for linear interpolation, otherwise nearest neighbor interpolation is used. |
| var | Pointer to the variable where the interpolated value will be stored. |
| sigma | Pointer to the variable where the standard deviation of the data points will be stored. |
array0 and array1 must be 2D arrays of size EX by EY. lons must have at least nlon elements and lats must have at least nlat elements.var will contain the interpolated value. sigma will contain the standard deviation of the data points used in the interpolation.lons. locate_reg, LIN, and NN for locating indices and performing interpolation.EX and EY are defined appropriately to match the dimensions of array0 and array1.Definition at line 2491 of file mptrac.c.
| void jsec2time | ( | const double | jsec, |
| int * | year, | ||
| int * | mon, | ||
| int * | day, | ||
| int * | hour, | ||
| int * | min, | ||
| int * | sec, | ||
| double * | remain | ||
| ) |
Converts Julian seconds to calendar date and time components.
This function converts Julian seconds to calendar date and time components, including year, month, day, hour, minute, and second. It also calculates the fractional part of the seconds.
| jsec | Julian seconds to convert. |
| year | Pointer to store the year. |
| mon | Pointer to store the month. |
| day | Pointer to store the day. |
| hour | Pointer to store the hour. |
| min | Pointer to store the minute. |
| sec | Pointer to store the second. |
| remain | Pointer to store the fractional part of seconds. |
The function initializes a time structure t0 with a fixed starting date and time. It then converts the Julian seconds to a time_t type by adding the seconds to the epoch time. Next, it converts the time_t value to a UTC time structure t1. Finally, it extracts the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second components from t1 and calculates the fractional part of seconds, which is stored in remain.
Definition at line 2582 of file mptrac.c.
| double kernel_weight | ( | const double | kz[EP], |
| const double | kw[EP], | ||
| const int | nk, | ||
| const double | p | ||
| ) |
Calculates the kernel weight based on altitude and given kernel data.
This function calculates the kernel weight based on altitude and given kernel data. It takes arrays of altitudes (kz) and corresponding weights (kw), the number of data points (nk), and the current altitude (p) as input.
| kz | Array of altitudes. |
| kw | Array of corresponding weights. |
| nk | Number of data points. |
| p | Current altitude. |
If the number of data points is less than 2 (nk < 2), the function returns a default weight of 1.0.
The function first computes the altitude z based on the current altitude p. Then it checks whether z is outside the range of altitudes in the kernel data. If so, it returns the corresponding weight at the nearest altitude boundary. Otherwise, it interpolates linearly between the two closest altitudes in the kernel data to determine the weight at altitude z.
Definition at line 2615 of file mptrac.c.
| double lapse_rate | ( | const double | t, |
| const double | h2o | ||
| ) |
Calculates the moist adiabatic lapse rate in Kelvin per kilometer.
This function calculates the moist adiabatic lapse rate in Kelvin per kilometer from the given temperature (t) in Kelvin and water vapor volume mixing ratio (h2o).
| t | Temperature in Kelvin. |
| h2o | Water vapor volume mixing ratio. |
The moist adiabatic lapse rate is calculated using the formula:
\[ \Gamma = \frac{{1000 \times g \times \left(a + L_v \times r \times T\right)}} {{C_{pd} \times a + L_v^2 \times r \times \epsilon}} \]
where:
The constants used in the calculation are defined externally:
Definition at line 2641 of file mptrac.c.
| void level_definitions | ( | ctl_t * | ctl | ) |
Defines pressure levels for meteorological data.
This function defines pressure levels for meteorological data based on the given control structure (ctl). Pressure levels are defined differently based on the value of press_level_def in ctl.
| ctl | Control structure containing information about pressure level definitions. |
The function determines the number of pressure levels (met_np) and the corresponding pressure values (met_p) based on the value of press_level_def in the control structure ctl. It initializes the met_np and met_p fields accordingly.
press_level_def are:press_level_def will result in an error message.Definition at line 2659 of file mptrac.c.
| int locate_irr | ( | const double * | xx, |
| const int | n, | ||
| const double | x | ||
| ) |
Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in a sorted array.
This function locates the index of the interval containing a given value in a sorted array. It uses a binary search algorithm to efficiently find the interval.
| xx | Pointer to the sorted array. |
| n | Size of the array. |
| x | Value to be located. |
x.The function assumes that the array xx is sorted in ascending order. It returns the index of the interval where the value x is located. If the value x is outside the range of the array, the function returns the index of the closest interval.
Definition at line 2869 of file mptrac.c.
| int locate_irr_float | ( | const float * | xx, |
| const int | n, | ||
| const double | x, | ||
| const int | ig | ||
| ) |
Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in an irregularly spaced array.
This function performs a binary search to locate the interval in the array xx such that xx[ig] <= x < xx[ig + 1]. If the value x lies within the interval specified by the initial guess index ig, the function returns ig. Otherwise, it searches the array to find the correct interval.
| xx | Pointer to the array of floats representing the irregularly spaced intervals. The array must be of size n. |
| n | The number of elements in the array xx. |
| x | The value to locate within the intervals of the array xx. |
| ig | The initial guess index. If the interval [xx[ig], xx[ig+1]) contains x, the function returns ig directly. |
i such that xx[i] <= x < xx[i + 1]. If x is out of bounds, it returns the index of the closest interval.xx contains at least two elements. xx.xx is not sorted in either increasing or decreasing order, or if it contains less than two elements.Definition at line 2899 of file mptrac.c.
| int locate_reg | ( | const double * | xx, |
| const int | n, | ||
| const double | x | ||
| ) |
Locate the index of the interval containing a given value in a regular grid.
This function locates the index of the interval containing a given value in a regular grid. It calculates the index based on the spacing between grid points and the value to be located.
| xx | Pointer to the array representing the regular grid. |
| n | Size of the grid (number of grid points). |
| x | Value to be located. |
x.The function assumes that the array xx represents a regular grid with equally spaced points. It calculates the index of the interval where the value x is located based on the spacing between grid points. If the value x is outside the range of the grid, the function returns the index of the closest interval.
Definition at line 2933 of file mptrac.c.
| void locate_vert | ( | float | profiles[EX][EY][EP], |
| const int | np, | ||
| const int | lon_ap_ind, | ||
| const int | lat_ap_ind, | ||
| const double | alt_ap, | ||
| int * | ind | ||
| ) |
Locate the four vertical indizes of a box for a given height value.
This function locates the vertical indices corresponding to a given height in a 3D irregular grid. It calculates the indices based on the specified longitude and latitude indices of the grid.
| profiles | 3D array representing the irregular grid. |
| np | Size of the profile (number of data points). |
| lon_ap_ind | Index of the longitude. |
| lat_ap_ind | Index of the latitude. |
| alt_ap | Height value. |
| ind | Pointer to an array to store the resulting indices. |
The function calculates the indices corresponding to the specified height in the 3D irregular grid. It stores the resulting indices in the array pointed to by ind. The indices are calculated based on the specified longitude and latitude indices of the grid.
Definition at line 2952 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_advect | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Advances particle positions using different advection schemes.
This function updates the positions of atmospheric particles using different advection schemes based on vertical velocity formulations (omega or zetadot). The advection is performed over a number of integration nodes, using meteorological data interpolated in time and space.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration settings. |
| [in] | cache | Pointer to the cache structure storing precomputed time step values. |
| [in] | met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the initial time. |
| [in] | met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle states. |
ctl->advect_vert_coord is 0 or 2, the function uses omega vertical velocity.ctl->advect_vert_coord is 1, the function uses zetadot vertical velocity.zeta values remain non-negative.Definition at line 2972 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_advect_init | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Initializes the advection module by setting up pressure fields.
This function initializes the advection module, setting up the air parcel pressure to be consistent with the given zeta vertical coordinate. It utilizes meteorological data from two time steps and interpolates the pressure values accordingly.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration flags. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the initial meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the final meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the air parcel data structure. |
The function performs the following operations:
Definition at line 3135 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_bound_cond | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Apply boundary conditions to particles based on meteorological and climatological data.
This function applies boundary conditions to particles based on specified criteria, including latitude, pressure, surface layer parameters, and climatological data. It loops over each particle and checks whether it satisfies the specified boundary conditions. If a particle satisfies the conditions, its properties such as mass, volume mixing ratio, and age of air are updated accordingly.
It checks for quantity flags to determine which properties need to be updated. If the latitude or pressure of a particle falls outside the specified ranges, it skips the particle. It also considers surface layer parameters such as surface pressure, height, zeta range, and planetary boundary layer. If a particle is within the specified surface layer boundaries, its properties are updated accordingly.
The function updates properties such as mass and volume mixing ratio if the corresponding flags are set. It retrieves volume mixing ratio values for various trace gases (e.g., CFC-10, CFC-11, N2O, SF6) from climatological time series data and updates the particle properties accordingly. Additionally, it updates the age of air for each particle based on the current simulation time.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatological data structure containing time series data. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the initial time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 3162 of file mptrac.c.

| void module_chem_grid | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Computes gridded chemical tracer concentrations (volume mixing ratio) from individual air parcel mass data and assigns them back to the parcels.
This function aggregates the mass of tracer particles onto a 3D chemical grid (longitude × latitude × altitude), accounting for either single or ensemble simulations depending on ctl->nens. It then interpolates meteorological temperature fields and computes volume mixing ratios, storing them in the specified tracer quantity (e.g., ctl->qnt_Cx).
If the molar mass is undefined or required quantity indices are missing, the function exits early.
Parallelization is supported via OpenMP or OpenACC.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration parameters, including grid dimensions, tracer indices, and simulation mode. |
| [in] | met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the beginning of the interpolation interval. |
| [in] | met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the end of the interpolation interval. |
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric state, including parcel coordinates, time, mass, and output tracer fields. |
| [in] | t | Central time step used for output and interpolation. |
ctl->molmass > 0, and ctl->qnt_m and ctl->qnt_Cx to be set.ctl->nens > 0 and assigns each parcel to its ensemble member via ctl->qnt_ens.qnt_Cx) is given in ppbv.Definition at line 3258 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_chem_init | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Initializes the chemistry modules by setting atmospheric composition.
This function initializes various chemical components of the atmosphere using meteorological data and climatological information. It interpolates and sets values for water vapor (H2O), ozone (O3), and several radical species such as OH, HO2, H2O2, and O1D for each air parcel.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing quantity flags. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing climatological data. |
| met0 | Pointer to the initial meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the final meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the air parcel data structure. |
The function uses OpenMP for parallel processing, iterating over each point in the atmosphere (atm->np) to initialize chemical species concentrations. It performs the following steps:
Definition at line 3420 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_convection | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Performs convective mixing of atmospheric particles.
This function adjusts the pressure of atmospheric particles based on boundary layer (PBL) mixing and convective conditions driven by CAPE (Convective Available Potential Energy) and CIN (Convective Inhibition). It uses meteorological data and random numbers for vertical mixing calculations.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure with simulation settings. |
| [in,out] | cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| [in,out] | met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the initial timestep. |
| [in,out] | met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the subsequent timestep. |
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure with particle properties. |
atm structure in place.Definition at line 3462 of file mptrac.c.
Manages domain decomposition and particle communication in parallel processing.
The module_dd function orchestrates the domain decomposition process, including particle assignment, sorting, transformation, and communication across MPI processes. It handles the initialization of particles, their assignment to subdomains, and communication between neighbouring processes.
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| cache | A pointer to a cache_t structure used for storing intermediate values. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information. |
| met | A pointer to a pointer of a met_t structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
dd_assign_rect_subdomains_atm.dd_sort.atm2particles.dd_communicate_particles.dd_particles2atm.ctl, atm, cache, dd, and met structures are properly initialized. It is designed to work in a parallel processing environment using MPI.Simulate exponential decay processes for atmospheric particles.
This function simulates decay processes for atmospheric particles based on their mass or volume mixing ratio. It loops over each particle and calculates the decay rate using weighting factors for tropospheric and stratospheric lifetimes. Exponential decay is then calculated, and the mass or volume mixing ratio of particles is updated accordingly. Loss rates can also be calculated and updated based on the decay process.
The function checks for quantity flags to ensure that mass or volume mixing ratio data is available. It then calculates the weighting factor based on the particle's location in the atmosphere and sets the lifetime accordingly. Exponential decay is calculated using the time step and the lifetime, and the particle's mass or volume mixing ratio is updated. Loss rates can also be updated based on the decay process.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climate data structure containing atmospheric data. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 3575 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_diff_meso | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Simulate mesoscale diffusion for atmospheric particles.
This function simulates mesoscale diffusion for atmospheric particles, including horizontal and vertical wind fluctuations. It calculates standard deviations of local wind data and temporal correlations for mesoscale fluctuations. Mesoscale wind fluctuations are then calculated based on the provided random numbers and turbulence parameters. The particle positions are updated accordingly.
The function loops over each particle and calculates indices for interpolation of wind data. It then computes standard deviations of local wind data and temporal correlations for mesoscale fluctuations. Based on the turbulence parameters and provided random numbers, it calculates horizontal and vertical mesoscale wind fluctuations. Finally, it updates the particle positions based on the calculated wind fluctuations.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
TURB_MESOX and TURB_MESOZ define the subgrid-scale variability as a fraction of the grid-scale variance. Stohl et al. (2005) recommend a default value of 0.16 for both parameters, providing a standard approach for turbulence representation. However, recent findings by Bakels et al. (2024) suggest disabling this approach to improve model accuracy under certain conditions. It is advised to evaluate the applicability of these recommendations based on the specific simulation context and objectives.Definition at line 3614 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_diff_pbl | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Computes particle diffusion within the planetary boundary layer (PBL).
This function handles the effects of turbulence on particles within the PBL. It calculates turbulent velocity variances, Lagrangian timescales, and updates particle positions and perturbations based on random fluctuations and boundary layer physics. This module adapts the approach of Ryall and Maryon (1998) and Stohl et al. (2005).
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing model settings. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure for the current timestep. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure for the next timestep. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle states. |
The function:
module_rng.sig_u, sig_w), their vertical derivatives, and Lagrangian timescales (tau_u, tau_w).The function uses OpenACC directives for GPU acceleration.
Definition at line 3691 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_diff_turb | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Applies turbulent diffusion processes to atmospheric particles.
This function calculates and applies turbulent diffusion effects, including horizontal and vertical diffusion, as well as vertical mixing in the planetary boundary layer (PBL), to a set of atmospheric particles based on input parameters and environmental conditions.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| [in,out] | cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| [in] | clim | Pointer to the climate structure containing climatological data. |
| [in,out] | met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure for the initial timestep. |
| [in,out] | met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure for the next timestep. |
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric structure containing particle data. |
The function performs the following operations:
Turbulent diffusivity parameters are derived from control inputs and weighted based on atmospheric layer influences (PBL, troposphere, stratosphere).
TURB_DX_PBL, TURB_DX_TROP, TURB_DX_STRAT, TURB_DZ_TROP and TURB_DZ_PBL, TURB_DZ_TROP, TURB_DZ_STRAT define horizontal and vertical diffusivities (in units of m**2 s**-1) in the PBL, troposphere, and stratosphere, respectively. The control parameter DIFF_MIX_PBL is used to switch vertical mixing in the PBL on or off.Definition at line 3816 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_dry_depo | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Simulate dry deposition of atmospheric particles.
This function simulates the dry deposition of atmospheric particles, including both particulate matter and gases. It calculates the sedimentation velocity for particles based on the atmospheric properties and applies it to determine the loss of mass or volume mixing ratio due to deposition. The function loops over each particle and calculates the loss of mass or volume mixing ratio based on the deposition velocity and time step.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 3868 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_h2o2_chem | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Perform chemical reactions involving H2O2 within cloud particles.
This function simulates chemical reactions involving hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) within cloud particles. It calculates the change in H2O2 concentration over time due to chemical reactions. The reaction rates are determined based on temperature and cloud properties such as liquid water content.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatological data structure. |
| met0 | Pointer to the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the second meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 3931 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_isosurf_init | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Initialize the isosurface module based on atmospheric data.
This function initializes the isosurface module based on the atmospheric data provided. It calculates the necessary variables required for generating the isosurface, such as pressure, density, or potential temperature. Additionally, it can read balloon pressure data from a file if specified in the control structure. The initialized data is stored in the cache for later use.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for storing initialized data. |
Definition at line 4013 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_isosurf | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Apply the isosurface module to adjust atmospheric properties.
This function applies the isosurface module to adjust atmospheric properties based on the initialized data stored in the cache. It interpolates and restores atmospheric pressure, density, or potential temperature according to the specified isosurface mode in the control structure.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 4083 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_kpp_chem | ( | ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
KPP chemistry module.
Simulate chemical reactions using the Kinetic PreProcessor (KPP) integration scheme.
This function simulates chemical reactions using the Kinetic PreProcessor (KPP) integration scheme for atmospheric particles. It loops over each particle in the atmospheric data structure and integrates chemical reactions over a specified time step using the KPP algorithm.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatological data structure. |
| met0 | Pointer to the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the second meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
| void module_meteo | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Update atmospheric properties using meteorological data.
This function updates atmospheric properties based on meteorological data interpolated between two time steps. It calculates various atmospheric quantities such as pressure, temperature, wind speed, humidity, etc., and updates the corresponding fields in the atmospheric data structure.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climate data structure containing climatological data. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data structure at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 4189 of file mptrac.c.
Update atmospheric properties through interparcel mixing.
This function updates atmospheric properties by performing interparcel mixing based on the given meteorological and climatological data. It calculates the indices of grid boxes and performs mixing for various quantities such as mass, volume mixing ratio, and other chemical species concentrations.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| clim | Pointer to the climate data structure containing climatological data. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
| t | Time at which mixing is performed. |
Definition at line 4296 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_mixing_help | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const int * | ixs, | ||
| const int * | iys, | ||
| const int * | izs, | ||
| const int | qnt_idx, | ||
| const int | use_ensemble | ||
| ) |
Perform subgrid-scale interparcel mixing of a given quantity.
This function computes the average of a specified quantity within each subgrid box (and optionally for each ensemble member) and applies a mixing adjustment to particle values based on the computed local mean.
The mixing accounts for differences in tropopause and stratosphere mixing via a weighted parameterization. It supports both ensemble and non-ensemble modes using the use_ensemble flag.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to control/configuration structure. |
| [in] | clim | Pointer to climatological data structure. |
| [in,out] | atm | Pointer to atmospheric state (includes particles). |
| [in] | ixs | Array of x-grid indices for each particle. |
| [in] | iys | Array of y-grid indices for each particle. |
| [in] | izs | Array of z-grid indices for each particle (-1 for invalid). |
| [in] | qnt_idx | Index of the quantity in atm->q to be mixed. |
| [in] | use_ensemble | Flag indicating whether to use ensemble-aware logic (0 = no, 1 = yes). |
izs[ip] < 0 are excluded from mixing. ctl->qnt_ens to be valid if use_ensemble is true.Definition at line 4367 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_oh_chem | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Perform hydroxyl chemistry calculations for atmospheric particles.
This function calculates the OH chemistry for each atmospheric particle based on the specified reaction mechanism and updates the particle quantities accordingly. The OH chemistry includes bimolecular and termolecular reactions, and the reaction rates are calculated based on the provided climatological data and atmospheric conditions. The function supports both mass and volume mixing ratio quantities for the particles.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climate data structure containing climatological data. |
| met0 | Pointer to the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the second meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 4469 of file mptrac.c.

Update the positions and pressure levels of atmospheric particles.
This function updates the positions and pressure levels of atmospheric particles based on the meteorological data and the specified time step. It loops over each particle in the atmospheric data structure and performs the following operations:
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the second meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 4553 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_rng_init | ( | const int | ntask | ) |
Initialize random number generators for parallel tasks.
This function initializes random number generators for parallel tasks using both GSL (GNU Scientific Library) and cuRAND (NVIDIA CUDA Random Number Generation Library) if available. It sets up GSL random number generators for each OpenMP thread and initializes them with unique seeds. For cuRAND, it creates a pseudo-random number generator and sets its seed. The initialization ensures that each task or thread has its own independent random number generator to prevent interference between parallel executions.
| ntask | The number of tasks or parallel threads for which random number generators are initialized. |
Definition at line 4604 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_rng | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| double * | rs, | ||
| const size_t | n, | ||
| const int | method | ||
| ) |
Generate random numbers using various methods and distributions.
This function generates random numbers using different methods and distributions based on the specified method and random number generator type. It supports uniform and normal distributions and can utilize GSL, Squares (Widynski, 2022), or cuRAND random number generators.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing parameters and settings. |
| rs | Pointer to the array where the generated random numbers will be stored. |
| n | The number of random numbers to generate. |
| method | The method for generating random numbers:
|
Definition at line 4635 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_sedi | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Simulate sedimentation of particles in the atmosphere.
This function calculates the sedimentation velocity of particles based on atmospheric pressure, temperature, and particle properties such as radius and density. It then updates the pressure of each particle based on the sedimentation velocity and the specified time step.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing parameters and settings. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the current time step. |
| met1 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the next time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data containing particle information. |
sedi function, which takes atmospheric pressure, temperature, particle radius, and particle density as inputs. DZ2DP function.Definition at line 4740 of file mptrac.c.
Sort particles according to box index.
This function sorts particles within the atmosphere data structure based on their geographical coordinates (longitude and latitude) and pressure level. It allocates temporary arrays to store indices and auxiliary data for sorting, then performs the sorting operation. After sorting, it updates the order of particles in the atmosphere data structure.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing parameters and settings. |
| met0 | Pointer to the meteorological data at the current time step. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data containing particle information. |
locate_reg and locate_irr functions to determine the appropriate index for sorting particles based on their longitude, latitude, and pressure level. Definition at line 4769 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_sort_help | ( | double * | a, |
| const int * | p, | ||
| const int | np | ||
| ) |
Reorder an array based on a given permutation.
This function reorders the elements of a given array based on a specified permutation array. It allocates temporary memory to store the reordered elements, performs the reordering operation, and then updates the original array with the reordered elements.
| a | Pointer to the array to be reordered. |
| p | Pointer to the permutation array defining the order of elements. |
| np | The number of elements in the array. |
p, which defines the new order of elements in the array a.Definition at line 4834 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_timesteps | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Calculate time steps for air parcels based on specified conditions.
This function calculates the time steps for air parcels based on specified conditions, including the direction of simulation, start and stop times, and a given target time. It adjusts the time step for each air parcel accordingly and checks for horizontal boundary conditions of local meteorological data.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the initial meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing air parcel information. |
| t | The target time for which time steps are calculated. |
t. Definition at line 4872 of file mptrac.c.
Initialize start time and time interval for time-stepping.
This function initializes the start time and time interval for time-stepping based on the direction of simulation and the provided atmospheric data. It sets the start time according to the minimum or maximum time in the atmospheric data, depending on the simulation direction. Additionally, it checks the time interval and adjusts the start time accordingly for rounding purposes.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing air parcel information. |
Definition at line 4919 of file mptrac.c.
| void module_tracer_chem | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Simulate chemical reactions involving long-lived atmospheric tracers.
This function simulates chemical reactions involving atmospheric tracers, such as CFC-10, CFC-11, CFC-12, and N2O. It calculates the change in tracer concentrations over time based on reaction rates and environmental factors such as temperature, ozone concentration, solar zenith angle, and O(1D) volume mixing ratio.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatological data structure. |
| met0 | Pointer to the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the second meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing particle information. |
Definition at line 4950 of file mptrac.c.
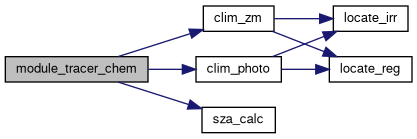
| void module_wet_depo | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Perform wet deposition calculations for air parcels.
This function calculates the wet deposition process for each air parcel based on provided atmospheric and meteorological data. It estimates the precipitation rate and scavenging coefficients for particles and gases inside and below cloud layers. The scavenging coefficients are used to calculate the exponential decay of mass or volume mixing ratio over time due to wet deposition.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing simulation parameters. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure for temporary data and random numbers. |
| met0 | Pointer to the initial meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the updated meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing air parcel information. |
Definition at line 5021 of file mptrac.c.
| void mptrac_alloc | ( | ctl_t ** | ctl, |
| cache_t ** | cache, | ||
| clim_t ** | clim, | ||
| met_t ** | met0, | ||
| met_t ** | met1, | ||
| atm_t ** | atm, | ||
| dd_t ** | dd | ||
| ) |
Allocates and initializes memory resources for MPTRAC.
This function handles memory allocation for various data structures and sets up GPU resources if available. It also creates the necessary data regions on GPUs for OpenACC-enabled execution.
| [out] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure (ctl_t). |
| [out] | cache | Pointer to the cache structure (cache_t). |
| [out] | clim | Pointer to the climatology structure (clim_t). |
| [out] | met0 | Pointer to the first meteorology structure (met_t). |
| [out] | met1 | Pointer to the second meteorology structure (met_t). |
| [out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t). |
| [out] | dd | pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
| Runtime | error if no GPU devices are available when OpenACC is enabled. |
Definition at line 5156 of file mptrac.c.
| void mptrac_free | ( | ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| dd_t * | dd | ||
| ) |
Frees memory resources allocated for MPTRAC.
This function releases the memory allocated for various data structures and deletes any associated data regions on GPUs if OpenACC is enabled.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | cache | Pointer to the cache structure (cache_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | clim | Pointer to the climatology structure (clim_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | met0 | Pointer to the first meteorology structure (met_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | met1 | Pointer to the second meteorology structure (met_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t) to be freed. |
| [in] | dd | Pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
Definition at line 5209 of file mptrac.c.
| void mptrac_get_met | ( | ctl_t * | ctl, |
| clim_t * | clim, | ||
| const double | t, | ||
| met_t ** | met0, | ||
| met_t ** | met1, | ||
| dd_t * | dd | ||
| ) |
Retrieves meteorological data for the specified time.
This function retrieves meteorological data for the given time t and updates the provided pointers to the met0 and met1 structures accordingly. It handles both the initialization and subsequent updates of the meteorological data based on the direction of time integration.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration settings. |
| clim | Pointer to the climate structure. |
| t | The current time for which meteorological data is to be retrieved. |
| met0 | Pointer to the pointer of the first meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the pointer of the second meteorological data structure. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
The function performs the following steps:
ctl, clim, met0, and met1 are properly initialized before calling this function.Definition at line 5242 of file mptrac.c.
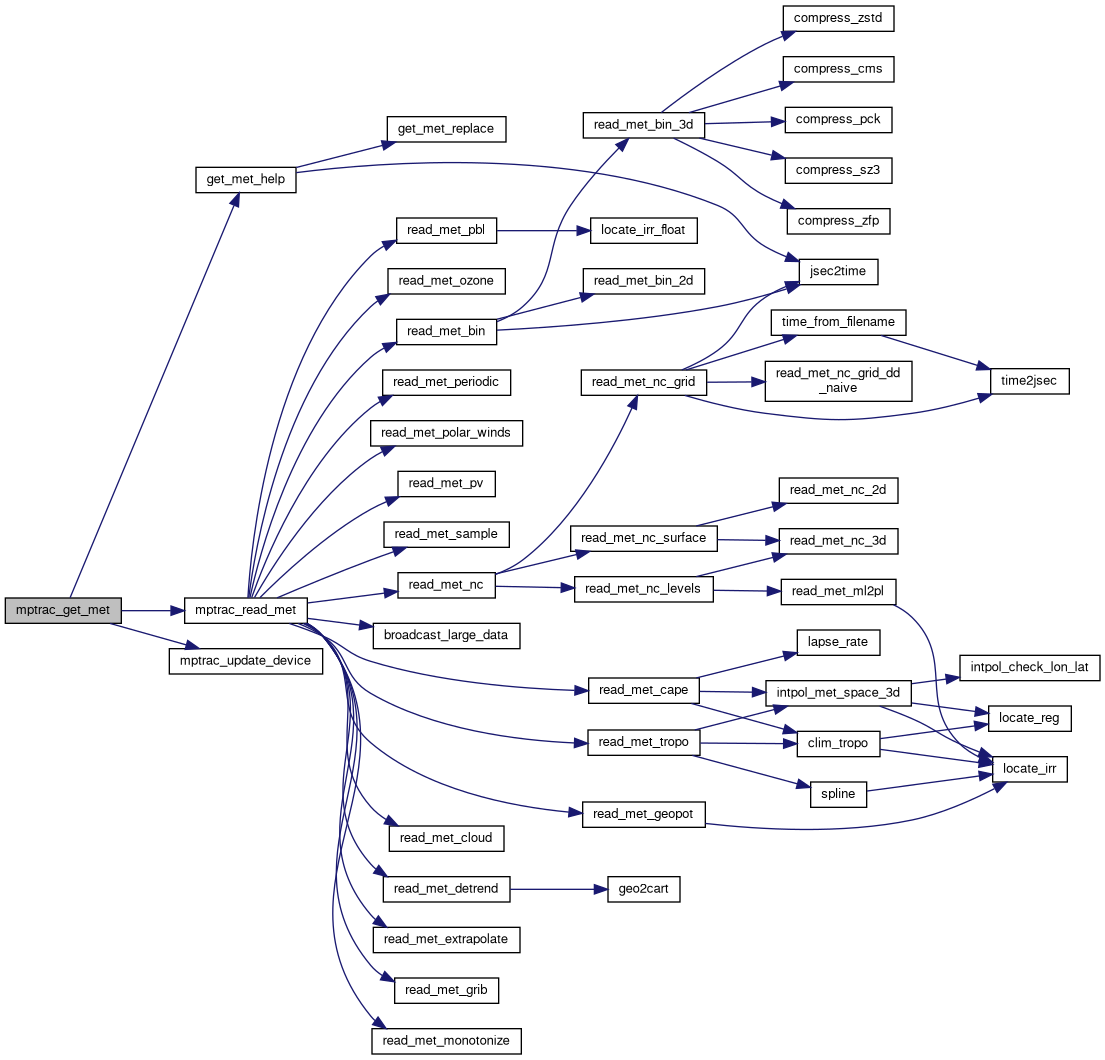
Initializes the MPTRAC model and its associated components.
This function sets up the necessary components and subsystems for the MPTRAC module, including timesteps, random number generation, and GPU memory updates.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration and state information. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure used for data storage and retrieval. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing climate-related data. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric structure containing atmospheric state data. |
| ntask | Number of tasks or threads to initialize for the random number generator. |
The function performs the following operations:
module_timesteps_init function.module_rng_init function.mptrac_update_device function.Definition at line 5364 of file mptrac.c.
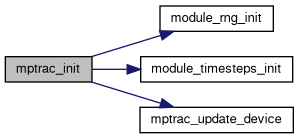
Reads air parcel data from a specified file into the given atmospheric structure.
This function reads air parcel data from a file and populates the provided atm_t structure based on the type of data specified in the ctl_t control structure. It supports various data formats including ASCII, binary, netCDF, and CLaMS.
| filename | The name of the file containing the atmospheric data. |
| ctl | A pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) that specifies the type of data. |
| atm | A pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t) that will be populated with the data. |
This function performs the following steps:
ctl->atm_type):0 for ASCII data1 for binary data2 for netCDF data3 or 4 for CLaMS dataThe function utilizes several helper functions and macros:
SELECT_TIMER for setting the timer.LOG for logging information.ERRMSG for handling error messages.gsl_stats_minmax for calculating minimum and maximum values.Z for converting altitude.Definition at line 5383 of file mptrac.c.
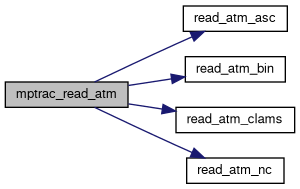
Reads various climatological data and populates the given climatology structure.
This function reads a range of climatological datasets based on the specified control settings and stores the data in the provided clim_t structure. It handles initialization of tropopause climatology, photolysis rates, and multiple gas species' climatologies and time series.
| ctl | A pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) that specifies file names and parameters for climatology data. |
| clim | A pointer to the climatology structure (clim_t) that will be populated with the data. |
This function performs the following steps:
ctl.ctl.ctl and applies a diurnal correction if specified.ctl.ctl.The function utilizes several helper functions:
clim_tropo_init for initializing tropopause climatology.read_clim_photo for reading photolysis rates.read_clim_zm for reading zonal mean climatologies.clim_oh_diurnal_correction for applying diurnal correction to OH climatology.read_clim_ts for reading time series data.Definition at line 5454 of file mptrac.c.
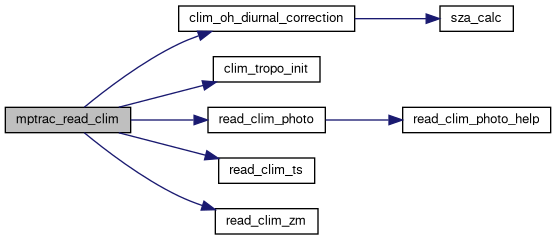
| void mptrac_read_ctl | ( | const char * | filename, |
| int | argc, | ||
| char * | argv[], | ||
| ctl_t * | ctl | ||
| ) |
Reads control parameters from a configuration file and populates the given structure.
This function reads control parameters from a specified configuration file and command line arguments, populating the provided ctl_t structure with the parsed data. It handles a wide range of parameters, performing necessary checks and providing default values where applicable.
| filename | A string containing the path to the configuration file. |
| argc | An integer representing the number of command line arguments. |
| argv | An array of strings containing the command line arguments. |
| ctl | A pointer to the structure (ctl_t) that will be populated with the control parameters. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 5514 of file mptrac.c.
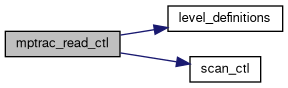
| int mptrac_read_met | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| dd_t * | dd | ||
| ) |
Reads meteorological data from a file, supporting multiple formats and MPI broadcasting.
This function reads meteorological data from a file specified by the filename parameter. It supports both NetCDF and binary formats based on the met_type field in the ctl_t structure. The function can also handle parallel processing with MPI, broadcasting the data across ranks if required by the configuration.
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the file to read the meteorological data from. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure, which holds control parameters including the type of meteorological data, MPI sharing flags, and configuration details. |
| clim | A pointer to a clim_t structure, which contains climatological data to be used in the process, if applicable. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that will store the meteorological data read from the file. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
met_mpi_share flag is set in the control structure.ctl->met_type is 0, the data is read from a NetCDF file using the read_met_nc function.ctl->met_type is between 1 and 5 or 7, the data is read from a binary file using the read_met_bin function.ctl->met_type is 6, the data is read from grib files using the read_met_grib function.met_type is not recognized, an error message is generated.Definition at line 6409 of file mptrac.c.
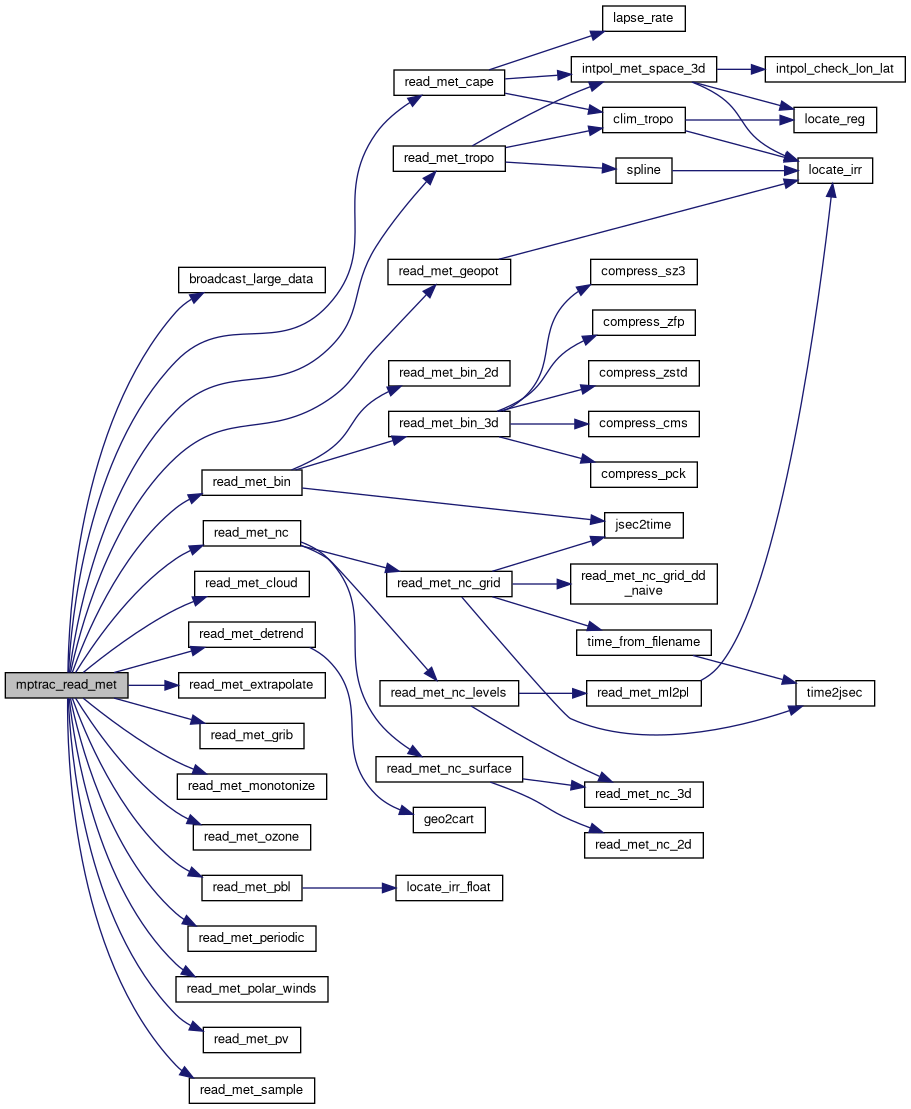
| void mptrac_run_timestep | ( | ctl_t * | ctl, |
| cache_t * | cache, | ||
| clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t ** | met0, | ||
| met_t ** | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| double | t, | ||
| dd_t * | dd | ||
| ) |
Executes a single timestep of the MPTRAC model simulation.
This function performs all operations required to advance the model simulation by one timestep. It includes updating air parcel positions, applying advection, diffusion, convection, and other processes such as sedimentation, chemistry, and deposition. Each process is conditionally executed based on the control settings provided in the ctl structure.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing model parameters and settings. |
| cache | Pointer to the cache structure used for intermediate calculations. |
| clim | Pointer to the climatology structure containing climatological data. |
| met0 | Pointer to the current meteorological data structure. |
| met1 | Pointer to the next meteorological data structure. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmosphere structure containing air parcel data. |
| t | Current simulation time in seconds. |
| dd | MPI information required for the domain decomposition. |
Definition at line 6518 of file mptrac.c.
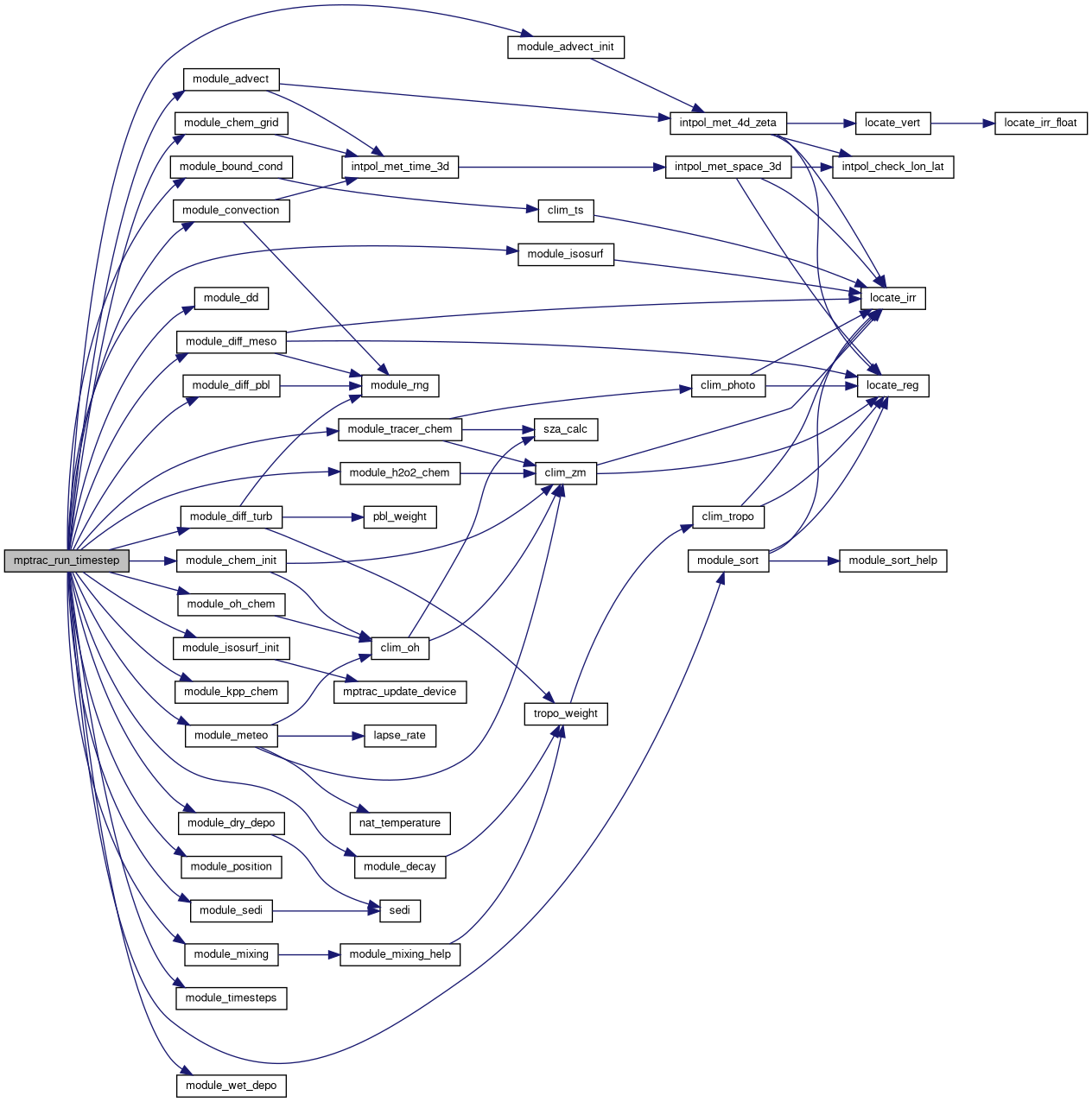
| void mptrac_write_atm | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes air parcel data to a file in various formats.
The mptrac_write_atm function writes the air parcel data stored in the atm structure to a file specified by filename. The format of the output file is determined by the atm_type_out field in the ctl control structure.
| filename | A string representing the name of the file to write the data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | The current time, used for certain output formats. |
The function performs the following steps:
SELECT_TIMER macro.atm_type_out value in the ctl structure, writes the data in one of the following formats:atm_type_out == 0): Calls write_atm_asc.atm_type_out == 1): Calls write_atm_bin.atm_type_out == 2): Calls write_atm_nc.atm_type_out == 3): Calls write_atm_clams_traj.atm_type_out == 4): Calls write_atm_clams.atm_type_out value is not supported, triggers an error message.ctl structure.Definition at line 6778 of file mptrac.c.
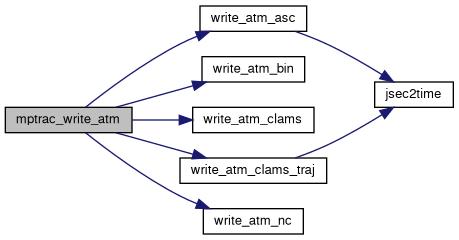
Writes meteorological data to a file, supporting multiple formats and compression options.
This function handles writing meteorological data based on the specified control (ctl_t) and meteorological data (met_t) structures. The file format and compression type are determined by the met_type in the control structure. The function supports netCDF, binary output, and various compression methods (ZFP, ZSTD, CMS), while providing error handling for unsupported configurations.
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the file to write the meteorological data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure, which holds the configuration and control parameters for the output, including the type of meteorological data and compression method. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that holds the meteorological data to be written to the file. |
ctl->met_type is 3, ZFP compression is required, and the function will generate an error if compiled without ZFP support.ctl->met_type is 4, ZSTD compression is required, and the function will generate an error if compiled without ZSTD support.ctl->met_type is 5, CMS compression is required, and the function will generate an error if compiled without CMS support.ctl->met_type is 7, SZ3 compression is required, and the function will generate an error if compiled without SZ3 support.ctl->met_type is 0, the function writes data in netCDF format via write_met_nc.ctl->met_type is between 1 and 5 or 7, the function writes data in binary format via write_met_bin.ctl->met_type is not recognized, an error message is generated.Definition at line 6838 of file mptrac.c.
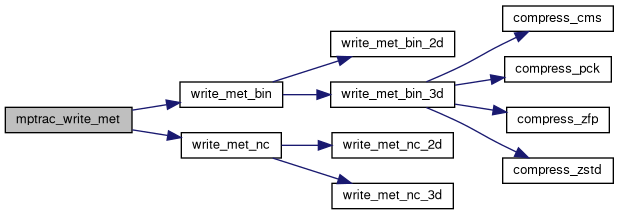
| void mptrac_write_output | ( | const char * | dirname, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes various types of output data to files in a specified directory.
The mptrac_write_output function writes various types of output data to files in the directory specified by the dirname parameter. The function takes control parameters (ctl), two meteorological data structures (met0 and met1), an atmospheric data structure (atm), and a time value (t) as input.
| dirname | A string representing the directory path where output files will be written. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met0 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the first set of meteorological data. |
| met1 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the second set of meteorological data. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure representing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double value representing the time at which the output is being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
t) to extract year, month, day, hour, minute, and second.Definition at line 6882 of file mptrac.c.
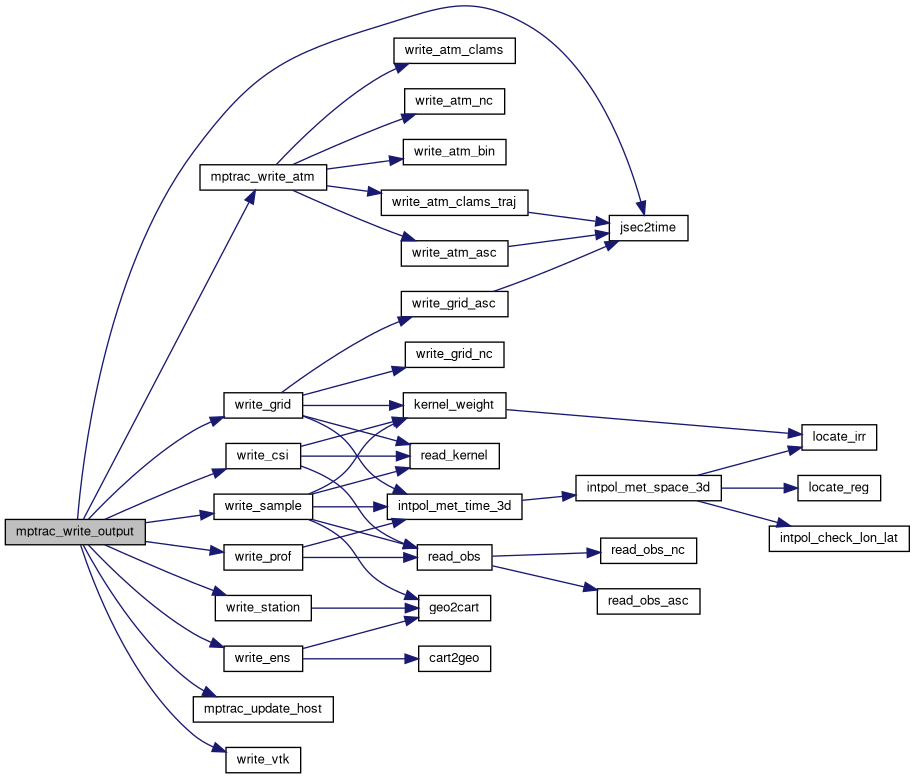
| void mptrac_update_device | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t ** | met0, | ||
| met_t ** | met1, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Updates device memory for specified data structures.
This function updates the GPU memory with the data from the provided host data structures (ctl, cache, clim, atm) using OpenACC directives. It ensures that the host data is transferred to the device for further computation.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the ctl_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for ctl is updated. |
| [in] | cache | Pointer to the cache_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for cache is updated. |
| [in] | clim | Pointer to the clim_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for clim is updated. |
| [in] | met0 | Pointer to the first met_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for met0 is updated. |
| [in] | met1 | Pointer to the second met_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for met1 is updated. |
| [in] | atm | Pointer to the atm_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding device memory for atm is updated. |
#pragma acc update directive for device memory synchronization. Each update operation is wrapped with a timer labeled as "UPDATE_DEVICE" for performance tracking.Definition at line 6666 of file mptrac.c.
| void mptrac_update_host | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const cache_t * | cache, | ||
| const clim_t * | clim, | ||
| met_t ** | met0, | ||
| met_t ** | met1, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm | ||
| ) |
Updates host memory for specified data structures.
This function transfers data from the device (GPU) memory back to the host memory for the provided data structures (ctl, cache, clim, atm) using OpenACC directives. It ensures that the latest data from the device is synchronized with the host.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the ctl_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for ctl is updated from the device. |
| [in] | cache | Pointer to the cache_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for cache is updated from the device. |
| [in] | clim | Pointer to the clim_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for clim is updated from the device. |
| [in] | met0 | Pointer to the first met_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for met0 is updated. |
| [in] | met1 | Pointer to the second met_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for met1 is updated. |
| [in] | atm | Pointer to the atm_t structure. If not NULL, the corresponding host memory for atm is updated from the device. |
#pragma acc update directive for host memory synchronization. Each update operation is wrapped with a timer labeled as "UPDATE_HOST" for performance tracking.Definition at line 6722 of file mptrac.c.
| double nat_temperature | ( | const double | p, |
| const double | h2o, | ||
| const double | hno3 | ||
| ) |
Calculates the nitric acid trihydrate (NAT) temperature.
This function computes the temperature at which nitric acid trihydrate (NAT) can form given the partial pressures of water vapor and nitric acid in the atmosphere.
| p | The total atmospheric pressure (in hPa). |
| h2o | The volume mixing ratio of water vapor (H2O). |
| hno3 | The volume mixing ratio of nitric acid (HNO3). |
This function follows these steps:
The calculations are based on empirical relationships involving logarithms of the partial pressures of H2O and HNO3.
Definition at line 6973 of file mptrac.c.
| double pbl_weight | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const int | ip, | ||
| const double | pbl, | ||
| const double | ps | ||
| ) |
Computes a weighting factor based on planetary boundary layer pressure.
This function calculates a weighting factor that determines the contribution of a pressure level to processes within the planetary boundary layer. The factor is based on the relative position of the pressure within a linear transition range defined by pbl and ps.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration parameters. |
| atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure containing pressure levels. |
| ip | Index of the pressure level in the atmospheric data array. |
| pbl | Pressure at the planetary boundary layer. |
| ps | Surface pressure. |
p0).p1).Definition at line 6997 of file mptrac.c.
Reads air parcel data from an ASCII file and populates the given atmospheric structure.
This function reads air parcel data from an ASCII file and stores the data in the provided atm_t structure. It reads each line of the file, extracts the necessary data fields, and converts the altitude to pressure.
| filename | The name of the ASCII file containing the atmospheric data. |
| ctl | A pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) that specifies the number of quantities. |
| atm | A pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t) that will be populated with the data. |
This function performs the following steps:
NP) and logs an error message if so.The function utilizes several macros and helper functions:
WARN for logging warnings.ERRMSG for handling error messages.TOK for tokenizing and reading values from the line.P for converting altitude to pressure.Definition at line 7019 of file mptrac.c.
Reads air parcel data from a binary file and populates the given atmospheric structure.
This function reads air parcel data from a binary file and stores the data in the provided atm_t structure. It checks the version of the binary data, reads the data values, and verifies the integrity of the data read.
| filename | The name of the binary file containing the atmospheric data. |
| ctl | A pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) that specifies the number of quantities. |
| atm | A pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t) that will be populated with the data. |
This function performs the following steps:
np).The function utilizes several macros and helper functions:
ERRMSG for handling error messages.FREAD for reading data from the binary file.Definition at line 7061 of file mptrac.c.
Reads atmospheric data from a CLAMS NetCDF file.
This function opens a NetCDF file, reads various atmospheric parameters, and stores them in the provided atm_t structure. It handles both zeta and pressure coordinate systems depending on the control settings.
| [in] | filename | Path to the NetCDF file containing atmospheric data. |
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure containing configuration settings. |
| [out] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure where the data will be stored. |
NPARTS).TIME_INIT) or falls back to time if unavailable.ctl->advect_vert_coord, reads ZETA and optionally PRESS, or reads PRESS_INIT with fallback to PRESS.LON) and latitude (LAT).Definition at line 7117 of file mptrac.c.
Reads air parcel data from a generic netCDF file and populates the given atmospheric structure.
This function reads air parcel data from a netCDF file and stores the data in the provided atm_t structure. It retrieves the dimensions, geolocations (time, pressure, longitude, latitude), and specified variables from the file.
| filename | The name of the netCDF file containing the atmospheric data. |
| ctl | A pointer to the control structure (ctl_t) that specifies the number of quantities and their names. |
| atm | A pointer to the atmospheric structure (atm_t) that will be populated with the data. |
This function performs the following steps:
np) from the "obs" dimension.atm_t structure.The function utilizes several macros and helper functions:
NC_INQ_DIM for inquiring about dimensions in the netCDF file.NC_GET_DOUBLE for reading double values from the netCDF file.NC for checking netCDF function return values.Definition at line 7177 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_clim_photo | ( | const char * | filename, |
| clim_photo_t * | photo | ||
| ) |
Reads photolysis rates from a NetCDF file and populates the given photolysis structure.
This function opens a NetCDF file specified by the filename, reads various dimensions and data related to photolysis rates, and stores this data in the provided clim_photo_t structure. It includes checks for data consistency and logs detailed information about the loaded data.
| filename | A string containing the path to the NetCDF file containing photolysis rate data. |
| photo | A pointer to the photolysis structure (clim_photo_t) that will be populated with the data. |
The function performs the following steps:
clim_photo_t structure.Definition at line 7210 of file mptrac.c.
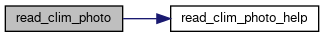
| void read_clim_photo_help | ( | const int | ncid, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const clim_photo_t * | photo, | ||
| double | var[CP][CSZA][CO3] | ||
| ) |
Reads a 3D climatological photochemistry variable from a NetCDF file.
This function reads a variable from a NetCDF file into a 3D array based on the dimensions provided by the clim_photo_t structure.
| [in] | ncid | NetCDF file ID. |
| [in] | varname | Name of the variable to read from the NetCDF file. |
| [in] | photo | Pointer to a structure defining the data dimensions (np, nsza, no3c). |
| [out] | var | 3D array to store the read data, with dimensions [CP][CSZA][CO3]. |
Definition at line 7301 of file mptrac.c.
| int read_clim_ts | ( | const char * | filename, |
| clim_ts_t * | ts | ||
| ) |
Reads a climatological time series from a file and populates the given time series structure.
This function reads time and volume mixing ratio (VMR) data from a specified file, processes the data, and stores it in the provided clim_ts_t structure. It also includes checks for data consistency and logs detailed information about the loaded data.
| filename | A string containing the path to the file containing the climatological time series data. |
| ts | A pointer to the time series structure (clim_ts_t) that will be populated with the data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7329 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_clim_zm | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| clim_zm_t * | zm | ||
| ) |
Reads zonally averaged climatological data from a netCDF file and populates the given structure.
This function reads data from a specified netCDF file, including pressure levels, latitudes, and volume mixing ratios (VMR) for a specified variable. It performs necessary checks and logs detailed information about the loaded data.
| filename | A string containing the path to the netCDF file. |
| varname | A string containing the name of the variable to be read from the netCDF file. |
| zm | A pointer to the structure (clim_zm_t) that will be populated with the data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7383 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_kernel | ( | const char * | filename, |
| double | kz[EP], | ||
| double | kw[EP], | ||
| int * | nk | ||
| ) |
Reads kernel function data from a file and populates the provided arrays.
This function reads kernel function data from a specified file, populating the provided arrays kz and kw with the parsed data. It also updates the variable pointed to by nk with the number of data points read. The function ensures that the height levels are in ascending order and performs checks for the number of height levels read.
| filename | A string containing the path to the file containing kernel function data. |
| kz | A double array to store the height levels of the kernel function. |
| kw | A double array to store the weights corresponding to the height levels. |
| nk | A pointer to an integer variable representing the number of data points read. |
The function performs the following steps:
nk with the number of data points read.Definition at line 7482 of file mptrac.c.
Reads meteorological data from a binary file.
This function reads meteorological data from a binary file and populates the provided met_t structure with the data. It checks the binary file's format version and met_type, ensuring compatibility with the control structure (ctl_t). The function reads time, grid, surface data, and multi-level data, and supports different binary file versions.
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the binary file to read the meteorological data from. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure that holds control parameters such as the expected met_type and other configuration options. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that will store the meteorological data read from the binary file. |
FREAD macro for safe binary reading operations, which checks the integrity of the read operation.met_type and binary file version to ensure compatibility.LSM, SST, RWC, SWC, and CC).met_type in the file does not match the ctl->met_type.Definition at line 7523 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_bin_2d | ( | FILE * | in, |
| const met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY], | ||
| const char * | varname | ||
| ) |
Reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a binary file and stores it in the provided array.
This function reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a binary file, which is assumed to be uncompressed, and stores it in the provided 2-dimensional array var. The variable name is used for logging purposes to identify the data being read.
| in | A pointer to the FILE structure representing the binary file to read from. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
| var | A 2-dimensional array to store the read variable. |
| varname | A string containing the name of the variable being read. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7671 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_bin_3d | ( | FILE * | in, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const float | bound_min, | ||
| const float | bound_max | ||
| ) |
Reads 3D meteorological data from a binary file, potentially using different compression methods.
This function reads 3-dimensional meteorological data from a binary file into a specified variable array. The data can be read in uncompressed form or using one of several supported compression methods. The data is then clamped to specified minimum and maximum bounds.
| [in] | in | Pointer to the input file from which to read the data. |
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure that contains metadata about the type of data and how it is stored. |
| [in] | met | Pointer to the meteorological structure that contains the dimensions of the data. |
| [out] | var | 3D array to store the read data, with dimensions [EX][EY][EP]. |
| [in] | varname | Name of the variable being read, used for logging and debugging. |
| [in] | bound_min | Minimum bound to which data values should be clamped. |
| [in] | bound_max | Maximum bound to which data values should be clamped. |
The function supports the following types of data:
Depending on the compression type specified in the control structure, the appropriate reading and decompression function is used. The data is read into a temporary buffer, then copied into the output array, applying the specified bounds to each value.
met structure. Definition at line 7700 of file mptrac.c.
Calculates Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE) for each grid point.
This function calculates the Convective Available Potential Energy (CAPE) at each grid point based on the provided meteorological data. CAPE is a measure of the energy available for deep convection, which is essential for severe weather development.
| ctl | Pointer to the control structure that contains metadata about the type of data and how it is stored. |
| clim | A pointer to a structure containing climatological data. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7806 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_cloud | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Calculates cloud-related variables for each grid point.
This function calculates cloud-related variables, such as cloud cover, cloud top pressure, cloud bottom pressure, and total cloud water content, based on the provided meteorological data.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7921 of file mptrac.c.
Detrends meteorological data.
This function detrends meteorological data by removing spatially varying backgrounds from each grid point. Detrending helps in removing systematic biases and trends from the data, enabling better analysis and modeling.
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 7978 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_extrapolate | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Extrapolates meteorological data.
This function extrapolates meteorological data by filling missing or invalid data points with values from the nearest valid point above. Extrapolation is performed column-wise, ensuring that missing data points are replaced with valid values.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8082 of file mptrac.c.
Calculates geopotential heights from meteorological data.
This function calculates geopotential heights from provided meteorological data using the hydrostatic equation. Geopotential heights are computed column-wise for each grid point based on the temperature, pressure, and surface height information. Optionally, the calculated geopotential heights can be smoothed horizontally using a weighted averaging scheme.
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8122 of file mptrac.c.
Reads meteorological data from a grib file and processes it.
This function reads meteorological data from a grib file specified by the filename parameter, using the ECCODES library. It reads grid, surface, and vertical level data, processes the data and calculates various derived meteorological fields such as geopotential heights, potential vorticity, cloud properties, and convective available potential energy (CAPE).
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the grib files to read the meteorological data from. The sf or ml suffixes indicating surface or multi-level data should be replaced with XX. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure, which contains control parameters for reading and processing the meteorological data. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that will store the meteorological data read and processed from the NetCDF file. |
| void read_met_grib_grid | ( | codes_handle ** | handles, |
| int | count_handles, | ||
| met_t * | met | ||
| ) |
Reads global meteorological information from a grib file.
This function reads meteorological grid information from a grib file, including time and spatial dimensions. The function computes the latitude and longitude grid based on the provided boundaries and increment values.
| handles | A pointer to an array of codes_handle pointers representing the grib messages. |
| count_handles | The total number of grib messages in the handles array. |
| met | A pointer to a structure to store meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
| void read_met_grib_levels | ( | codes_handle ** | handles, |
| const int | num_messages, | ||
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met | ||
| ) |
Reads meteorological variables at different vertical levels from a grib file.
This function reads meteorological variables such as temperature, wind components, specific humidity, ozone data, cloud parameters, and cloud cover at various vertical levels from a grib file.
| handles | A pointer to an array of codes_handle pointers representing the grib messages. |
| num_messages | The total number of grib messages in the handles array. |
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure to store meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
| void read_met_grib_surface | ( | codes_handle ** | handles, |
| const int | num_messages, | ||
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met | ||
| ) |
Reads surface meteorological data from a grib file and stores it in the meteorological data structure.
This function reads various surface meteorological variables from a grib file and stores them in the provided meteorological data structure. Depending on the configuration, it may read data for surface pressure, geopotential height, temperature, zonal and meridional wind components, land-sea mask, and sea surface temperature.
| handles | A pointer to an array of codes_handle pointers representing the grib messages. |
| num_messages | The total number of grib messages in the handles array. |
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure to store meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
| void read_met_ml2pl | ( | const ctl_t * | ctl, |
| const met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const char * | varname | ||
| ) |
Interpolates meteorological data to specified pressure levels.
This function interpolates meteorological data from model levels to pressure levels. The interpolation is performed in parallel over the spatial grid defined in the meteorological data structure.
| [in] | ctl | A pointer to a control structure containing the number of pressure levels (met_np) and the pressure levels themselves (met_p). |
| [in] | met | A pointer to a meteorological data structure containing the grid dimensions (nx, ny) and the pressure profile (pl). |
| [in,out] | var | A 3D array containing the meteorological variable to be interpolated. On output, this array will contain the interpolated values at the specified pressure levels. |
| [in] | varname | A string representing the name of the meteorological variable being interpolated. |
This function performs the following steps:
var array.Definition at line 9706 of file mptrac.c.
Makes zeta and pressure profiles monotone.
This function ensures that zeta and pressure profiles are monotone increasing and decreasing with altitude. It iterates over each grid point and each level to identify inversions and linearly interpolate between them to maintain monotonicity. The interpolation is performed for both zeta and pressure profiles.
| ctl | A pointer to a control parameter structure. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 9748 of file mptrac.c.
Reads meteorological data from a NetCDF file and processes it.
This function reads meteorological data from a NetCDF file specified by the filename parameter, using the NetCDF library. It reads grid, surface, and vertical level data, processes the data (including extrapolation, boundary conditions, and downsampling), and calculates various derived meteorological fields such as geopotential heights, potential vorticity, cloud properties, and convective available potential energy (CAPE).
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the NetCDF file to read the meteorological data from. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure, which contains control parameters for reading and processing the meteorological data. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that will store the meteorological data read and processed from the NetCDF file. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
nc_open and handles any errors during the file opening process.Definition at line 9833 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_nc_grid | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const int | ncid, | ||
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| dd_t * | dd | ||
| ) |
Reads meteorological grid data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition.
The read_met_nc_grid function reads meteorological data from NetCDF files and processes it with domain decomposition for parallel processing. It extracts time information, grid dimensions, and coordinates, and sets up hyperslabs for subdomains and halos. It also reads pressure levels and handles model level and surface data.
| filename | A string representing the filename of the NetCDF file to read. |
| ncid | A NetCDF file ID. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure where meteorological data will be stored. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8250 of file mptrac.c.
Read meteorological grid data from a NetCDF file and set up subdomain decomposition with halos.
This function initializes the distributed grid decomposition for meteorological data stored in a NetCDF file. It queries global grid dimensions (longitude, latitude), determines the local subdomain size for each MPI rank, and sets up hyperslabs for reading data in parallel. It also constructs halo regions for subdomain boundaries, ensuring periodic wrap-around in the zonal direction when applicable.
The function adjusts subdomain sizes at the right and bottom edges of the global grid to exactly fit the full domain. It then updates the met_t structure with the local longitude and latitude arrays for the subdomain including halos, and stores decomposition metadata in the dd_t structure.
| [out] | dd | Pointer to a dd_t structure. On output, it contains:
|
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to a ctl_t structure containing decomposition parameters:
|
| [out] | met | Pointer to a met_t structure. On output, it contains:
|
| [in] | ncid | NetCDF file ID obtained from a call to nc_open. |
-DMPI.Definition at line 9873 of file mptrac.c.
Reads and processes meteorological level data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition.
The read_met_nc_levels function reads meteorological level data from a NetCDF file and processes it for use in a domain decomposition context. It handles various meteorological parameters such as temperature, wind components, humidity, ozone, cloud data, and vertical velocity. The function also processes pressure levels and interpolates data between model and pressure levels as needed.
| ncid | An integer representing the NetCDF file ID. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters and settings. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure where meteorological level data will be stored. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8555 of file mptrac.c.
Reads and processes surface meteorological data from NetCDF files with domain decomposition.
The read_met_nc_surface function reads surface meteorological data from a NetCDF file and processes it for use in a domain decomposition context. It handles various surface parameters such as pressure, geopotential height, temperature, wind components, and other relevant meteorological data. The function is designed to work with different meteorological data formats and configurations.
| ncid | An integer representing the NetCDF file ID. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters and settings. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure where surface meteorological data will be stored. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8417 of file mptrac.c.
| int read_met_nc_2d | ( | const int | ncid, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const char * | varname2, | ||
| const char * | varname3, | ||
| const char * | varname4, | ||
| const char * | varname5, | ||
| const char * | varname6, | ||
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const met_t * | met, | ||
| dd_t * | dd, | ||
| float | dest[EX][EY], | ||
| const float | scl, | ||
| const int | init | ||
| ) |
Reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file.
This function reads a 2-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file and stores it in a specified destination array. It supports both packed and unpacked data formats and handles missing values and scaling factors accordingly. The function also checks the meteorological data layout to ensure correct data copying.
| ncid | The NetCDF file ID. |
| varname | The name of the variable to read. |
| varname2 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname is not found). |
| varname3 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname2 is not found). |
| varname4 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname3 is not found). |
| varname5 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname4 is not found). |
| varname6 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname5 is not found). |
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
| dest | The destination array to store the read data. |
| scl | A scaling factor to apply to the read data. |
| init | Flag indicating whether to initialize the destination array before reading. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 8752 of file mptrac.c.
| int read_met_nc_3d | ( | const int | ncid, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const char * | varname2, | ||
| const char * | varname3, | ||
| const char * | varname4, | ||
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const met_t * | met, | ||
| dd_t * | dd, | ||
| float | dest[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const float | scl | ||
| ) |
Reads a 3-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file.
This function reads a 3-dimensional meteorological variable from a NetCDF file and stores it in a specified destination array. It supports both packed and unpacked data formats and handles missing values and scaling factors accordingly. The function also checks the meteorological data layout to ensure correct data copying.
| ncid | The NetCDF file ID. |
| varname | The name of the variable to read. |
| varname2 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname is not found). |
| varname3 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname2 is not found). |
| varname4 | An alternative name of the variable to read (in case varname3 is not found). |
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
| dd | A pointer to an dd_t structure containing MPI information, including rank and neighbours. |
| dest | The destination array to store the read data. |
| scl | A scaling factor to apply to the read data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 9014 of file mptrac.c.
Computes the planetary boundary layer (PBL) pressure based on meteorological data.
This function determines the PBL pressure for each grid point using one of four methods: 0. Read PBL pressure from meteo data file.
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to the control structure (ctl_t), which contains parameters controlling the PBL calculation. |
| [in,out] | met | Pointer to the meteorological data structure (met_t), which contains grid and atmospheric data. The met->pbl array is updated with the calculated PBL pressure. |
Method 0 (Precomputed PBL pressure from file):
Method 1 (Precomputed PBL height from file):
Method 2 (Richardson number criterion):
Method 3 (Potential temperature difference):
Final Adjustments:
Definition at line 10113 of file mptrac.c.

| void read_met_periodic | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Applies periodic boundary conditions to meteorological data along longitudinal axis.
This function applies periodic boundary conditions to meteorological data along the longitudinal axis. It checks if the difference between the last and first longitudes and the difference between the second and first longitudes are approximately equal to 360 degrees, indicating periodicity. If the condition is met, the function increases the longitude counter, sets the longitude value for the new grid point, and copies meteorological data from the first grid point to the last grid point to ensure periodicity.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10250 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_polar_winds | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Applies a fix for polar winds in meteorological data.
This function applies a fix for polar winds in meteorological data, particularly focusing on the u and v wind components. It checks if the latitudes at the top and bottom of the grid are close to the poles. If so, it transforms the winds at 89-degree latitude into Cartesian coordinates, takes their mean, and replaces the winds at 90-degree latitude with this mean, effectively fixing the unrealistic behavior of winds at the poles.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10311 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_pv | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Calculates potential vorticity (PV) from meteorological data.
This function calculates the potential vorticity (PV) from the provided meteorological data. It employs finite difference methods to estimate gradients of temperature, wind components, and pressure in longitude, latitude, and pressure dimensions. These gradients are then used to compute PV at each grid point. Additionally, a fix for polar regions is applied to ensure smoothness of PV values in these regions.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10370 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_met_ozone | ( | met_t * | met | ) |
Calculates the total column ozone from meteorological ozone data.
This function calculates the total column ozone from the provided meteorological ozone data. It integrates ozone concentrations over altitude to obtain the column ozone density. The result is then converted to Dobson units, which represent the thickness of the ozone layer if compressed into one layer at standard temperature and pressure.
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological ozone data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10476 of file mptrac.c.
Downsamples meteorological data based on specified parameters.
This function downsamples meteorological data based on the provided control parameters. It reduces the resolution of meteorological data by averaging over specified intervals in longitude, latitude, and altitude.
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters for downsampling. |
| met | A pointer to a structure containing meteorological data to be downsampled. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10505 of file mptrac.c.
Calculates the tropopause and related meteorological variables based on various methods and stores the results in the meteorological data structure.
This function calculates the tropopause and related meteorological variables using different methods specified by the control parameters. The calculated tropopause pressure is stored in the provided meteorological data structure.
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| clim | A pointer to the climatological data structure. |
| met | A pointer to the meteorological data structure to store the calculated tropopause pressure and related variables. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10678 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_obs | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| double * | rt, | ||
| double * | rz, | ||
| double * | rlon, | ||
| double * | rlat, | ||
| double * | robs, | ||
| int * | nobs | ||
| ) |
Reads observation data from a file and stores it in arrays.
This function reads observation data from a specified file in either ASCII or NetCDF format, depending on the value of the OBS_TYPE control parameter. It stores the time, altitude, longitude, latitude, and observation values in the provided arrays.
| filename | The path to the observation data file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a structure containing control parameters. |
| rt | An array to store the time values of the observations. |
| rz | An array to store the altitude values of the observations. |
| rlon | An array to store the longitude values of the observations. |
| rlat | An array to store the latitude values of the observations. |
| robs | An array to store the observation values. |
| nobs | A pointer to an integer variable to store the number of observations read. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10850 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_obs_asc | ( | const char * | filename, |
| double * | rt, | ||
| double * | rz, | ||
| double * | rlon, | ||
| double * | rlat, | ||
| double * | robs, | ||
| int * | nobs | ||
| ) |
Reads observation data from an ASCII file.
This function reads observation data from a specified ASCII file. It extracts time, altitude, longitude, latitude, and observation values from each line of the file and stores them in the provided arrays.
| filename | The path to the ASCII file containing the observation data. |
| rt | An array to store the time values of the observations. |
| rz | An array to store the altitude values of the observations. |
| rlon | An array to store the longitude values of the observations. |
| rlat | An array to store the latitude values of the observations. |
| robs | An array to store the observation values. |
| nobs | A pointer to an integer variable to store the number of observations read. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10894 of file mptrac.c.
| void read_obs_nc | ( | const char * | filename, |
| double * | rt, | ||
| double * | rz, | ||
| double * | rlon, | ||
| double * | rlat, | ||
| double * | robs, | ||
| int * | nobs | ||
| ) |
Reads observation data from a NetCDF file.
This function reads observation data from a specified NetCDF file. It extracts time, altitude, longitude, latitude, and observation values from the variables in the NetCDF file and stores them in the provided arrays.
| filename | The path to the NetCDF file containing the observation data. |
| rt | An array to store the time values of the observations. |
| rz | An array to store the altitude values of the observations. |
| rlon | An array to store the longitude values of the observations. |
| rlat | An array to store the latitude values of the observations. |
| robs | An array to store the observation values. |
| nobs | A pointer to an integer variable to store the number of observations read. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10922 of file mptrac.c.
| double scan_ctl | ( | const char * | filename, |
| int | argc, | ||
| char * | argv[], | ||
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const int | arridx, | ||
| const char * | defvalue, | ||
| char * | value | ||
| ) |
Scans a control file or command-line arguments for a specified variable.
This function scans either a control file or command-line arguments for a specified variable name and retrieves its value. It searches for the variable name in the control file or command-line arguments and returns its corresponding value. If the variable is not found, it returns a default value specified by the user.
| filename | The name of the control file to be scanned. If NULL, only command-line arguments will be scanned. |
| argc | The number of command-line arguments. |
| argv | An array of command-line arguments. |
| varname | The name of the variable to be searched. |
| arridx | The index of the variable array, if applicable. Set to -1 if not an array. |
| defvalue | The default value to be returned if the variable is not found. |
| value | A pointer to a character array to store the retrieved value. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 10951 of file mptrac.c.
| double sedi | ( | const double | p, |
| const double | T, | ||
| const double | rp, | ||
| const double | rhop | ||
| ) |
Calculates the sedimentation velocity of a particle in air.
This function calculates the sedimentation velocity of a particle in air using the given parameters.
| p | The atmospheric pressure [hPa]. |
| T | The temperature [K]. |
| rp | The radius of the particle [microns]. |
| rhop | The density of the particle [kg/m^3]. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11023 of file mptrac.c.
| void spline | ( | const double * | x, |
| const double * | y, | ||
| const int | n, | ||
| const double * | x2, | ||
| double * | y2, | ||
| const int | n2, | ||
| const int | method | ||
| ) |
Performs spline interpolation or linear interpolation.
This function interpolates a set of data points using either cubic spline interpolation or linear interpolation, depending on the specified method.
| x | The array of x-coordinates of the data points. |
| y | The array of y-coordinates of the data points. |
| n | The number of data points. |
| x2 | The array of x-coordinates where interpolation is required. |
| y2 | The array to store the interpolated y-values. |
| n2 | The number of points to interpolate. |
| method | The interpolation method: 1 for cubic spline, 0 for linear interpolation. |
If the method is set to 1 (cubic spline interpolation):
If the method is set to 0 (linear interpolation):
Definition at line 11056 of file mptrac.c.
| float stddev | ( | const float * | data, |
| const int | n | ||
| ) |
Calculates the standard deviation of a set of data.
This function calculates the standard deviation of a set of floating-point data values.
| data | Pointer to the array of data values. |
| n | Number of data values in the array. |
The standard deviation is calculated using the formula:
\[ \sigma = \sqrt{\frac{\sum_{i=1}^{n} (x_i - \bar{x})^2}{n}} \]
where:
| void time2jsec | ( | const int | year, |
| const int | mon, | ||
| const int | day, | ||
| const int | hour, | ||
| const int | min, | ||
| const int | sec, | ||
| const double | remain, | ||
| double * | jsec | ||
| ) |
Converts time components to seconds since January 1, 2000, 12:00:00 UTC.
This function calculates the number of seconds elapsed since January 1, 2000, 12:00:00 UTC, based on the provided year, month, day, hour, minute, and second. It also includes a fractional part to represent the remaining seconds.
| year | The year. |
| mon | The month (1-12). |
| day | The day of the month (1-31). |
| hour | The hour of the day (0-23). |
| min | The minute (0-59). |
| sec | The second (0-59). |
| remain | The fractional part of seconds. |
| jsec | Pointer to store the calculated number of seconds since January 1, 2000, 12:00:00 UTC. |
The function calculates the time elapsed since January 1, 2000, 12:00:00 UTC, up to the specified time and includes any fractional seconds indicated by the "remain" parameter.
Definition at line 11124 of file mptrac.c.
| void timer | ( | const char * | name, |
| const char * | group, | ||
| const int | output | ||
| ) |
Measures and reports elapsed time for named and grouped timers.
The timer function measures elapsed time for a specified named timer and an optional group of timers, accumulating time statistics such as minimum, maximum, and mean elapsed times. It also provides an option to log the timing statistics to an output.
| name | A string representing the name of the timer. |
| group | A string representing the group to which the timer belongs. |
| output | An integer flag indicating whether to report the timing statistics (non-zero to report). |
The function keeps track of multiple timers and groups. When called, it:
output parameter is non-zero.name and group.name and group are new, and if so, initializes them.omp_get_wtime() to get the current wall time. NTIMER macro.NTIMER, the function will trigger an error message.Definition at line 11155 of file mptrac.c.
| double time_from_filename | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const int | offset | ||
| ) |
Extracts and converts a timestamp from a filename to Julian seconds.
The time_from_filename function parses a given filename to extract a timestamp and converts it to Julian seconds. The timestamp is expected to follow a specific format and position within the filename, defined by the offset parameter.
| filename | A string representing the filename containing the timestamp. |
| offset | An integer indicating the position from the end of the filename where the timestamp starts. |
The function performs the following steps:
time2jsec function.YYYY-MM-DD_HH-MM (e.g., "2023-05-27_14-45").Definition at line 11223 of file mptrac.c.
Computes a weighting factor based on tropopause pressure.
This function calculates a weighting factor for a given pressure value in relation to the tropopause pressure. The weighting factor is determined as follows:
| [in] | clim | Pointer to the climatology data structure. |
| [in] | atm | Pointer to the atmospheric data structure. |
| [in] | ip | Index of the pressure value to evaluate within the atmospheric data. |
Definition at line 11258 of file mptrac.c.
Writes air parcel data to an ASCII file or gnuplot.
The write_atm_asc function writes the atmospheric data stored in the atm structure to an ASCII file specified by filename or to pipe to gnuplot if requested.
| filename | A string representing the name of the file to write the data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | The current time used for filtering and timestamping. |
The function performs the following steps:
atm structure, filtering by time if specified, and writes the data to the output file.Definition at line 11281 of file mptrac.c.
Writes air parcel data to a binary file.
The write_atm_bin function writes the air parcel data stored in the atm structure to a binary file specified by filename. The function includes versioning information and ensures that all relevant data arrays are written in a consistent binary format.
| filename | A string representing the name of the file to write the data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
The function performs the following steps:
ctl structure and writes each quantity array to the file.Definition at line 11363 of file mptrac.c.
Writes air parcel data to a NetCDF file in the CLaMS format.
The write_atm_clams function creates a NetCDF file and writes air parcel data into it. The data includes time, latitude, longitude, pressure, and other specified quantities. The function defines the dimensions and variables, sets global attributes, and writes the data to the file.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11413 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_atm_clams_traj | ( | const char * | dirname, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes CLaMS trajectory data to a NetCDF file.
The write_atm_clams_traj function writes trajectory data for the CLaMS model to a NetCDF file. The file is created and populated with data including time, latitude, longitude, pressure, and other quantities. The function also handles the creation of a final initialization file at the last time step.
| dirname | A string representing the directory name where the file will be created. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | The current time in seconds since a reference epoch. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11466 of file mptrac.c.
Writes air parcel data to a NetCDF file.
The write_atm_nc function creates a NetCDF file and writes air parcel data into it. The data includes time, pressure, longitude, latitude, and other specified quantities. The function defines the dimensions and variables, sets global attributes, and writes the data to the file.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11624 of file mptrac.c.
Writes Critical Success Index (CSI) data to a file.
The write_csi function processes air parcel and observation data to calculate and write various verification statistics, including the Critical Success Index (CSI), to a specified output file at regular intervals. The statistics include measures such as the number of hits, misses, and false alarms, bias, probability of detection, false alarm rate, equitable threat score, and correlation coefficients.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double representing the current time. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11673 of file mptrac.c.
Writes ensemble-based Critical Success Index (CSI) and other verification statistics to an output file.
This function computes and writes various statistical verification metrics that assess the performance of ensemble forecasts compared to observations. The output includes, for each ensemble member:
On the first invocation (when t == ctl->t_start), the function loads observation data and kernel weights, allocates necessary arrays, and creates a new output file with a descriptive header. On the final call (when t == ctl->t_stop), the function closes the file and frees all persistent memory.
Output is written at time steps divisible by ctl->csi_dt_out.
| [in] | filename | Path to the output file where statistics will be written. |
| [in] | ctl | Pointer to control structure containing configuration, ensemble settings, and spatial/time grid info. |
| [in] | atm | Pointer to atmospheric data structure holding model output. |
| [in] | t | Current simulation/model time. |
| If | required quantities (mass or ensemble IDs) are undefined, if ensemble IDs are out of bounds, or if the output file cannot be created. |
Writes ensemble data to a file.
The write_ens function processes air parcel data to calculate ensemble means and standard deviations for various quantities and writes them to a specified output file. It handles ensemble members and calculates statistics such as means and standard deviations for each ensemble, along with latitude, longitude, altitude, and time information.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double representing the current time. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 11948 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_grid | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes grid data to a file in ASCII or netCDF format.
The write_grid function processes air parcel data to calculate various grid-based statistics such as column density, mean, and standard deviation for specified quantities. It then writes this data to a specified output file either in ASCII or netCDF format based on the configuration parameters provided in the ctl structure.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met0 | A pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data for the initial time step. |
| met1 | A pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data for the final time step. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure containing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double representing the current time. |
The function performs the following steps:
grid_type in the control parameters.Definition at line 12045 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_grid_asc | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const double * | cd, | ||
| double * | mean[NQ], | ||
| double * | sigma[NQ], | ||
| const double * | vmr_impl, | ||
| const double | t, | ||
| const double * | z, | ||
| const double * | lon, | ||
| const double * | lat, | ||
| const double * | area, | ||
| const double | dz, | ||
| const int * | np | ||
| ) |
Writes grid data to an ASCII file.
The write_grid_asc function writes gridded air parcel data, including column density, mean and standard deviation for specified quantities, and volume mixing ratio (if available), to an ASCII file. The function also supports writing gnuplot commands to generate plots if requested in the control parameters.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| cd | An array of doubles representing column density values. |
| mean | An array of arrays of doubles representing the mean values for specified quantities. |
| sigma | An array of arrays of doubles representing the standard deviation values for specified quantities. |
| vmr_impl | An array of doubles representing the volume mixing ratio (implicit) values. |
| t | A double representing the current time. |
| z | An array of doubles representing vertical coordinates (altitude). |
| lon | An array of doubles representing longitudinal coordinates. |
| lat | An array of doubles representing latitudinal coordinates. |
| area | An array of doubles representing surface area values. |
| dz | A double representing the layer depth. |
| np | An array of integers representing the number of particles. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 12236 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_grid_nc | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| const double * | cd, | ||
| double * | mean[NQ], | ||
| double * | sigma[NQ], | ||
| const double * | vmr_impl, | ||
| const double | t, | ||
| const double * | z, | ||
| const double * | lon, | ||
| const double * | lat, | ||
| const double * | area, | ||
| const double | dz, | ||
| const int * | np | ||
| ) |
Writes grid data to a NetCDF file.
The write_grid_nc function writes gridded air parcel data, including column density, mean and standard deviation for specified quantities, and volume mixing ratio (if available), to a NetCDF file. NetCDF is a self-describing, machine-independent data format for storing scientific data.
| filename | A string representing the name of the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| cd | An array of doubles representing column density values. |
| mean | An array of arrays of doubles representing the mean values for specified quantities. |
| sigma | An array of arrays of doubles representing the standard deviation values for specified quantities. |
| vmr_impl | An array of doubles representing the volume mixing ratio (implicit) values. |
| t | A double representing the current time. |
| z | An array of doubles representing vertical coordinates (altitude). |
| lon | An array of doubles representing longitudinal coordinates. |
| lat | An array of doubles representing latitudinal coordinates. |
| area | An array of doubles representing surface area values. |
| dz | A double representing the layer depth. |
| np | An array of integers representing the number of particles. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 12340 of file mptrac.c.
Writes meteorological data in binary format to a specified file.
This function writes meteorological data from the met_t structure to a binary file. The data includes grid and surface data, as well as multi-level data such as temperature, velocity components, and atmospheric properties. The compression options for multi-level data (ZFP) are controlled via the ctl_t structure. The function supports multiple variables, such as surface pressure, temperature, wind components, and cloud properties.
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the file to write the binary data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure, which holds control parameters including the type of meteorological data, compression settings, and grid dimensions. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that contains the meteorological data to be written to the binary file. |
ctl->met_type) and the version of the binary format are written at the beginning of the file.write_met_bin_2d helper function.write_met_bin_3d function with optional ZFP compression settings.Definition at line 12470 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_met_bin_2d | ( | FILE * | out, |
| met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY], | ||
| const char * | varname | ||
| ) |
Writes a 2-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file.
The write_met_bin_2d function writes a 2-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file specified by the out parameter. The variable data is provided in a 2-dimensional array var with maximum dimensions EX by EY. The variable name is provided as a string in the varname parameter.
| out | A pointer to a FILE structure representing the output file. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data. |
| var | An array of floats representing the 2-dimensional variable data. |
| varname | A string containing the name of the variable being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
var to the temporary buffer help.out.Definition at line 12582 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_met_bin_3d | ( | FILE * | out, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const char * | varname, | ||
| const int | precision, | ||
| const double | tolerance | ||
| ) |
Writes a 3-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file.
The write_met_bin_3d function writes a 3-dimensional meteorological variable to a binary file specified by the out parameter. The variable data is provided in a 3-dimensional array var with maximum dimensions EX by EY by EP. The variable name is provided as a string in the varname parameter. Additionally, the function takes parameters for specifying the compression precision and tolerance.
| out | A pointer to a FILE structure representing the output file. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure containing meteorological data. |
| var | An array of floats representing the 3-dimensional variable data. |
| varname | A string containing the name of the variable being written. |
| precision | An integer specifying the precision of compression (for certain compression methods). |
| tolerance | A double specifying the tolerance for compression (for certain compression methods). |
The function performs the following steps:
var to the temporary buffer help.out using the specified compression method (uncompressed, packed, ZFP, ZSTD, cmultiscale).ctl->met_type, the function writes the variable data using different compression methods. If ctl->met_type is not supported, an error message is logged.Definition at line 12611 of file mptrac.c.
Writes meteorological data to a NetCDF file.
This function creates and writes meteorological data to a NetCDF file in the NetCDF-4 format. It defines the required dimensions, grid, surface variables, and level data within the NetCDF structure and writes the corresponding values from the met_t structure. The function uses helper functions to write 2D surface and 3D level data.
| filename | A constant character pointer representing the name of the NetCDF file to create and write the data to. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure that contains control parameters, such as the NetCDF level and quantization settings. |
| met | A pointer to a met_t structure that contains the meteorological data to be written to the NetCDF file. |
Definition at line 12701 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_met_nc_2d | ( | const int | ncid, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY], | ||
| const float | scl | ||
| ) |
Writes a 2D meteorological variable to a NetCDF file.
This function writes a 2D meteorological variable, stored in the array var, to a NetCDF file with the specified variable name. The data is scaled by a factor scl before being written. The function handles memory allocation for the data copy, scaling, and freeing the allocated memory after writing the data to the NetCDF file.
| ncid | The NetCDF file ID. This is an integer that identifies the NetCDF file where the data will be written. It is assumed that this file has already been opened for writing. |
| varname | A pointer to a string containing the name of the variable in the NetCDF file where the data will be stored. |
| met | A pointer to a structure of type met_t that contains metadata about the meteorological field, including the dimensions nx (number of points in x-direction) and ny (number of points in y-direction). |
| var | A 2D array of dimensions EX x EY containing the meteorological data to be written. The data is provided in the format var[ix][iy], where ix is the index in the x-direction and iy is the index in the y-direction. |
| scl | A scaling factor applied to each element in the var array before writing to the NetCDF file. |
Definition at line 12865 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_met_nc_3d | ( | const int | ncid, |
| const char * | varname, | ||
| met_t * | met, | ||
| float | var[EX][EY][EP], | ||
| const float | scl | ||
| ) |
Writes a 3D meteorological variable to a NetCDF file.
This function writes a 3D meteorological variable, stored in the array var, to a NetCDF file with the specified variable name. The data is scaled by a factor scl before being written. The function handles memory allocation for the data copy, scaling, and freeing the allocated memory after writing the data to the NetCDF file.
| ncid | The NetCDF file ID. This is an integer that identifies the NetCDF file where the data will be written. It is assumed that this file has already been opened for writing. |
| varname | A pointer to a string containing the name of the variable in the NetCDF file where the data will be stored. |
| met | A pointer to a structure of type met_t that contains metadata about the meteorological field, including the dimensions nx (number of points in the x-direction), ny (number of points in the y-direction), and np (number of points in the third dimension, e.g., pressure levels). |
| var | A 3D array of dimensions EX x EY x EP containing the meteorological data to be written. The data is provided in the format var[ix][iy][ip], where ix is the index in the x-direction, iy is the index in the y-direction, and ip is the index in the third dimension (e.g., vertical levels). |
| scl | A scaling factor applied to each element in the var array before writing to the NetCDF file. |
Definition at line 12894 of file mptrac.c.
| void write_prof | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes profile data to a specified file.
The write_prof function writes profile data to a file specified by the filename parameter. It takes control parameters (ctl), two meteorological data structures (met0 and met1), an atmospheric data structure (atm), and a time value (t) as input.
| filename | A string representing the filename where the profile data will be written. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met0 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the first set of meteorological data. |
| met1 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the second set of meteorological data. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure representing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double value representing the time at which the profile data is being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 12924 of file mptrac.c.
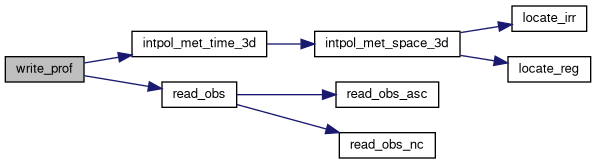
| void write_sample | ( | const char * | filename, |
| const ctl_t * | ctl, | ||
| met_t * | met0, | ||
| met_t * | met1, | ||
| const atm_t * | atm, | ||
| const double | t | ||
| ) |
Writes sample data to a specified file.
The write_sample function writes sample data to a file specified by the filename parameter. It takes control parameters (ctl), two meteorological data structures (met0 and met1), an atmospheric data structure (atm), and a time value (t) as input.
| filename | A string representing the filename where the sample data will be written. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| met0 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the first set of meteorological data. |
| met1 | A pointer to a met_t structure representing the second set of meteorological data. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure representing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double value representing the time at which the sample data is being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 13151 of file mptrac.c.
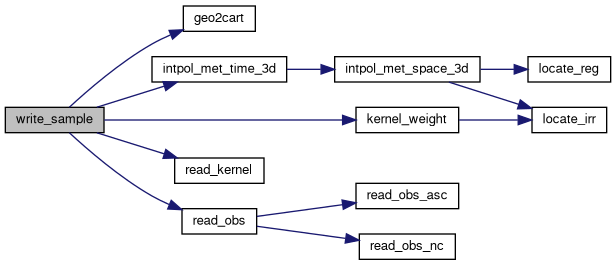
Writes station data to a specified file.
The write_station function writes station data to a file specified by the filename parameter. It takes control parameters (ctl), an atmospheric data structure (atm), and a time value (t) as input.
| filename | A string representing the filename where the station data will be written. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure representing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double value representing the time at which the station data is being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 13313 of file mptrac.c.
Writes VTK (Visualization Toolkit) data to a specified file.
The write_vtk function writes VTK data to a file specified by the filename parameter. It takes control parameters (ctl), an atmospheric data structure (atm), and a time value (t) as input.
| filename | A string representing the filename where the VTK data will be written. |
| ctl | A pointer to a ctl_t structure containing control parameters. |
| atm | A pointer to an atm_t structure representing atmospheric data. |
| t | A double value representing the time at which the VTK data is being written. |
The function performs the following steps:
Definition at line 13399 of file mptrac.c.